快速學(xué)習(xí)一個算法,CNN
大家好,我是小寒
今天給大家介紹一個強(qiáng)大的算法模型,CNN
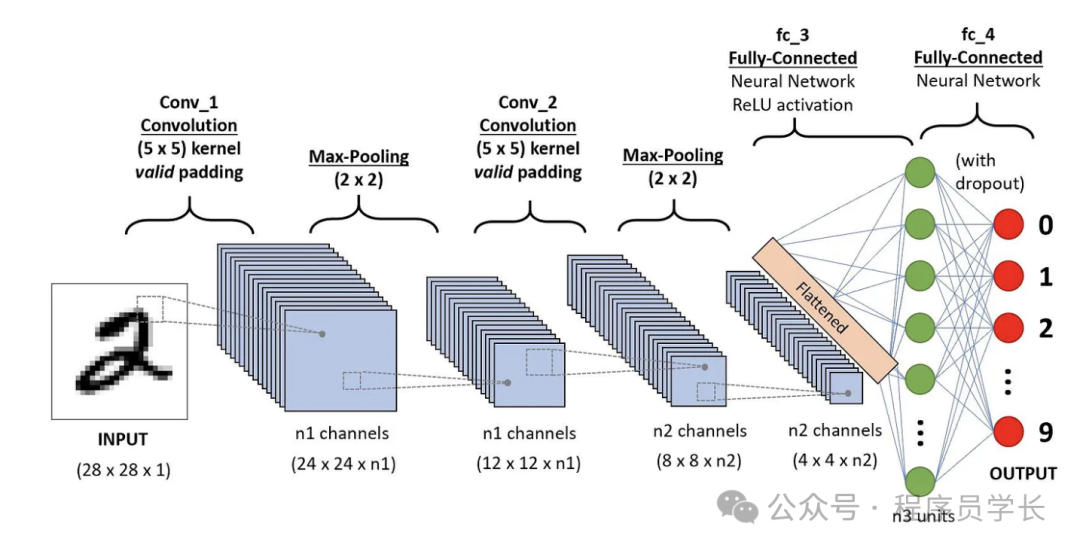
卷積神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò) (CNN) 是一類深度學(xué)習(xí)算法,主要用于處理和分析視覺數(shù)據(jù)。
它們徹底改變了計算機(jī)視覺領(lǐng)域,使圖像識別、物體檢測和各種其他應(yīng)用取得了突破。
什么是卷積神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)?
卷積神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò) (CNN) 是一種人工神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò),專門用于處理結(jié)構(gòu)化網(wǎng)格數(shù)據(jù)(例如圖像)。
與將輸入視為平面像素陣列的傳統(tǒng)神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)不同,CNN 利用圖像的空間結(jié)構(gòu)來提取分層特征。這種能力使 CNN 在圖像分類、對象檢測和分割等任務(wù)中特別有效。
 圖片
圖片
關(guān)鍵組件
1.卷積層
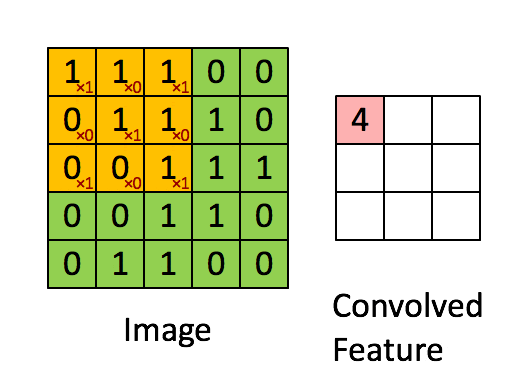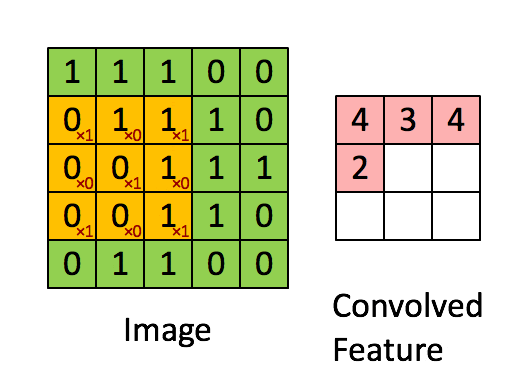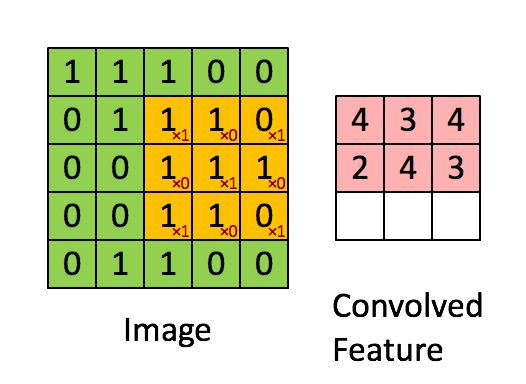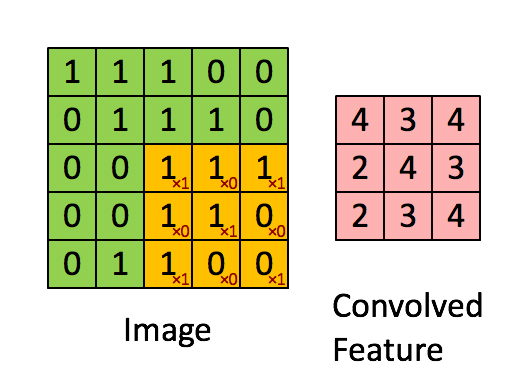
卷積層是 CNN 的核心組件,用于提取輸入數(shù)據(jù)的特征。
卷積層通過濾波器(卷積核)在輸入數(shù)據(jù)上滑動,進(jìn)行卷積操作,生成特征圖(Feature Map)。每個卷積核負(fù)責(zé)捕捉圖像的不同特征,如邊緣、紋理等。
 圖片
圖片
- 卷積核
檢測特定特征(如邊緣、紋理或圖案)的小矩陣。常見尺寸為 3x3 或 5x5。 - 步幅
卷積核在輸入圖像上移動的步長。步幅為 1 表示卷積核每次移動一個像素。 - 填充
在輸入圖像的邊框周圍添加額外的像素,以確保卷積核正確適配。
 圖片
圖片
以下是使用 NumPy 的簡單實(shí)現(xiàn)。
import numpy as np
def convolve(image, kernel, stride=1, padding=0):
# Add padding to the input image
image_padded = np.pad(image, [(padding, padding), (padding, padding)], mode='constant', constant_values=0)
# Calculate output dimensions
output_height = (image.shape[0] - kernel.shape[0] + 2 * padding) // stride + 1
output_width = (image.shape[1] - kernel.shape[1] + 2 * padding) // stride + 1
# Initialize output
output = np.zeros((output_height, output_width))
# Perform convolution
for i in range(0, output_height, stride):
for j in range(0, output_width, stride):
output[i, j] = np.sum(image_padded[i:i+kernel.shape[0], j:j+kernel.shape[1]] * kernel)
return output2.池化層
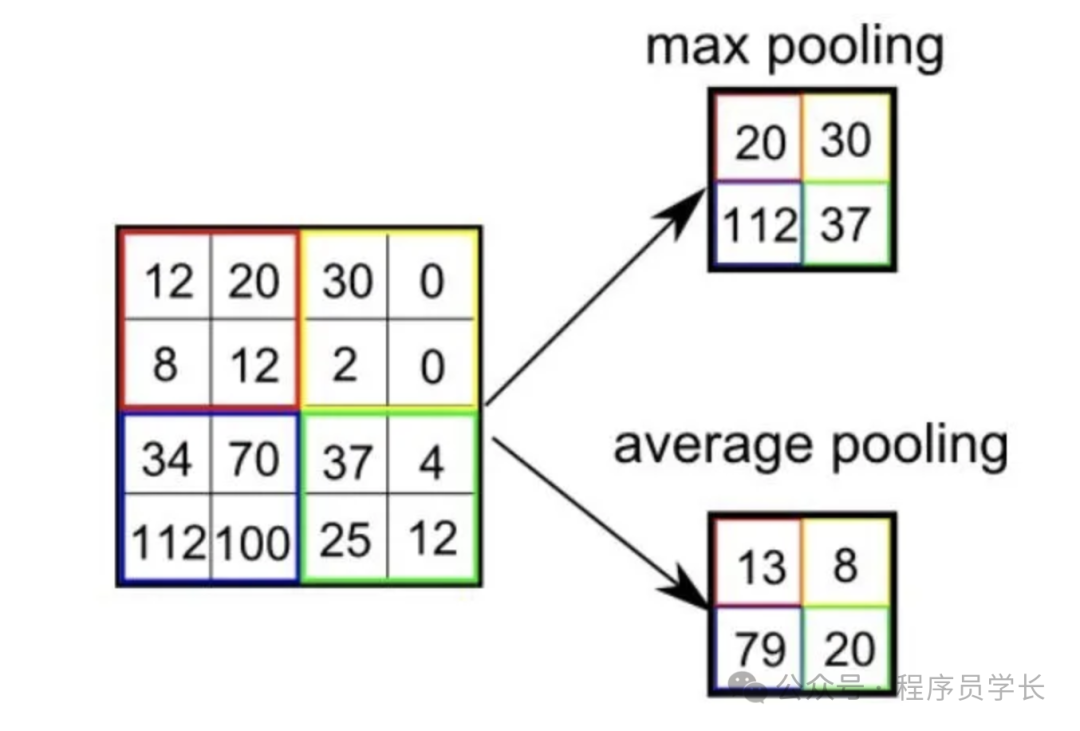
池化層通常用于降低特征圖的空間尺寸(高度和寬度),減少參數(shù)數(shù)量和計算復(fù)雜性,同時使特征檢測更加魯棒。
池化操作主要有兩種類型:
- 最大池化:從特征圖的每個塊中獲取最大值。
- 平均池化:從特征圖的每個塊中取平均值。
 圖片
圖片
def max_pooling(image, size=2, stride=2):
output_height = (image.shape[0] - size) // stride + 1
output_width = (image.shape[1] - size) // stride + 1
output = np.zeros((output_height, output_width))
for i in range(0, output_height, stride):
for j in range(0, output_width, stride):
output[i, j] = np.max(image[i:i+size, j:j+size])
return output3.全連接層
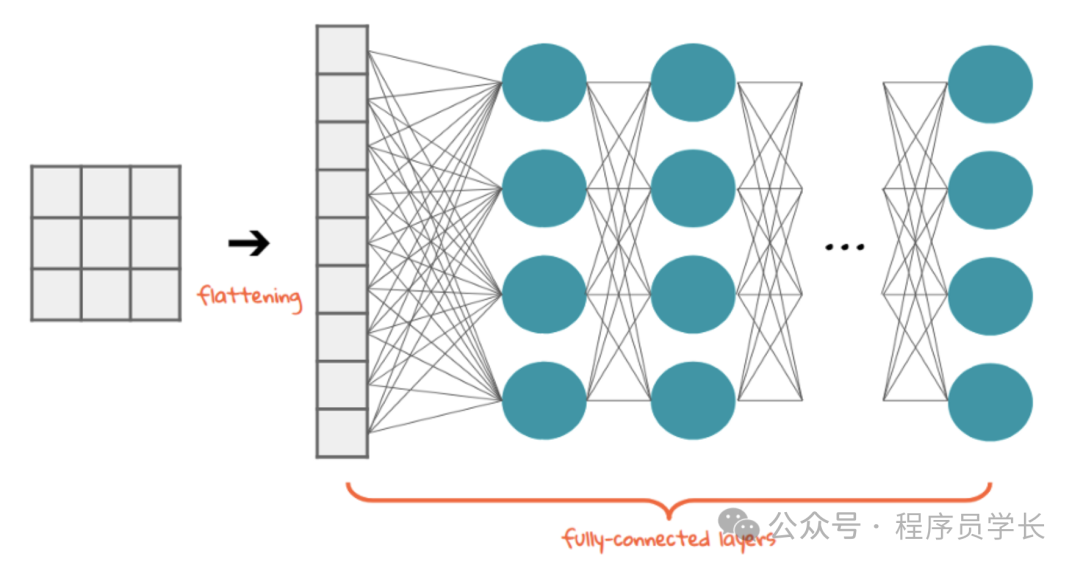
經(jīng)過幾個卷積層和池化層之后,神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)中的高級推理通過全連接層完成。
這些層將扁平化的特征圖作為輸入,并將其用于最終分類。
 圖片
圖片
CNN 的執(zhí)行過程
讓我們通過一個例子來了解 CNN 如何處理圖像:
- 輸入圖像
考慮 32x32x3 RGB 圖像(高度、寬度、深度)。 - 卷積層
對圖像應(yīng)用多個過濾器(例如 3x3),從而產(chǎn)生多個特征圖。假設(shè)我們使用 10 個過濾器;輸出將為 32x32x10。 - 池化層
使用 2x2 最大池化,步長為 2,以減少空間維度。輸出將為 16x16x10。 - 額外的卷積和池化層
根據(jù)需要重復(fù)卷積、激活和池化操作。 - 全連接層
將最后一個池化層的輸出展平(例如,8x8x10 變?yōu)?640 維向量)并將其連接到密集層以進(jìn)行分類。 - 輸出層
應(yīng)用softmax函數(shù)獲取類別的概率分布。
下面我們將使用 TensorFlow 構(gòu)建一個簡單的 CNN,用于 MNIST 數(shù)據(jù)集(手寫數(shù)字?jǐn)?shù)據(jù)集)的圖像分類。
首先我們導(dǎo)入必要的庫
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import layers, models
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt然后加載和預(yù)處理數(shù)據(jù)
# Load the MNIST dataset
(train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = tf.keras.datasets.mnist.load_data()
# Normalize the images
train_images = train_images.reshape((60000, 28, 28, 1)).astype('float32') / 255
test_images = test_images.reshape((10000, 28, 28, 1)).astype('float32') / 255構(gòu)建 CNN 模型
model = models.Sequential([
layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activatinotallow='relu', input_shape=(28, 28, 1)),
layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)),
layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activatinotallow='relu'),
layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)),
layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activatinotallow='relu'),
layers.Flatten(),
layers.Dense(64, activatinotallow='relu'),
layers.Dense(10, activatinotallow='softmax')
])
model.summary()編譯并訓(xùn)練模型
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
history = model.fit(train_images, train_labels, epochs=5,
validation_data=(test_images, test_labels))評估模型
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(test_images, test_labels)
print(f"Test accuracy: {test_acc}")
plt.plot(history.history['accuracy'], label='accuracy')
plt.plot(history.history['val_accuracy'], label='val_accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.show()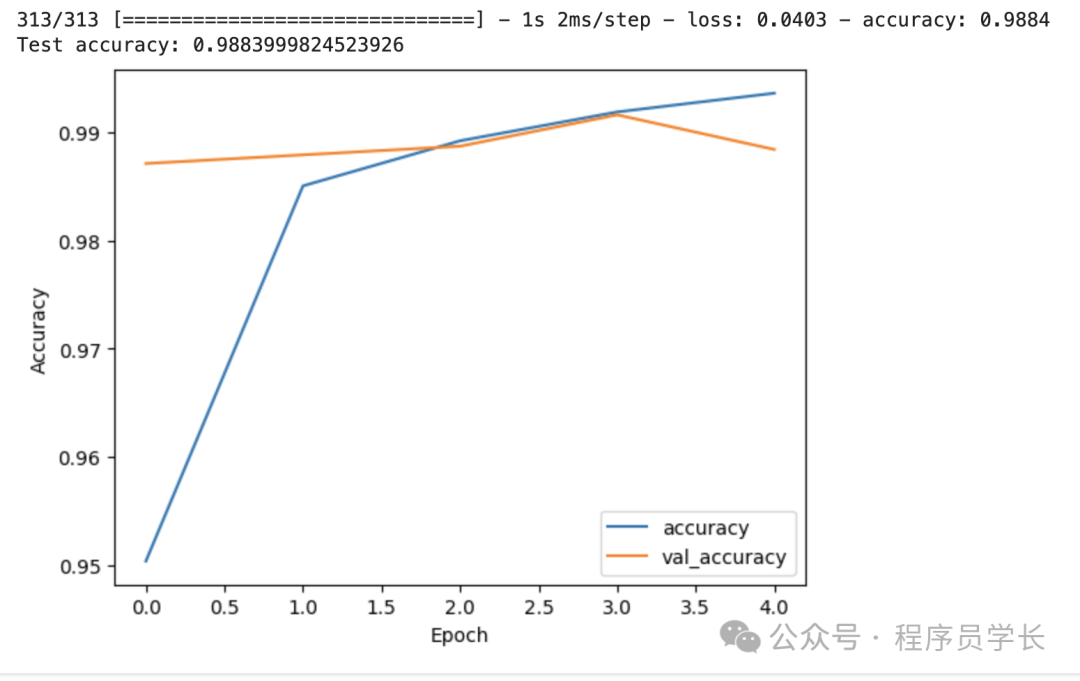 圖片
圖片












































