使用本地部署的Hermes 2 Pro構建開放的LLM應用程序
譯文譯者 | 布加迪
審校 | 重樓
之前我介紹了如何使用OpenAI最新的LLM GPT-4o,通過函數調用將實時數據引入到LLM。在這篇后續文章中我將介紹使用Hermes 2 Pro -Llama- 3 8B進行函數調用,這是一種由Nous Research開發的功能強大的LLM,基于Meta的Llama 3架構,有80億個參數。它是開放模型,我們將在Hugging Face的文本生成推理上運行它。
我們將把Fightaware.com的API 與該LLM集成起來,以便實時跟蹤航班狀態。
FlightAware的AeroAPI是開發人員獲取全面航班信息的一種完美工具。它支持實時航班跟蹤、歷史和未來航班數據以及按各種標準進行航班搜索。該API以用戶友好的JSON格式呈現數據,因而高度可用、易于集成。我們將調用REST API,根據用戶發送給LLM的提示獲取航班的實時狀態。
Hermes 2 Pro簡介
Hermes 2 Pro -Llama- 3 8B擅長自然語言處理任務、創意寫作和編程協助等。它的一項突出功能是出色的函數調用功能,便于執行外部函數,并檢索與股票價格、公司基本面、財務報表等相關的信息。
該模型利用特殊的系統提示和多輪函數調用結構以及新的ChatML角色,使得函數調用可靠且易于解析。據基準測試顯示,Hermes 2 Pro-Llama-3在與Fireworks AI合作構建的函數調用評估中獲得了出色的90%。
本地部署Hermes 2 Pro
就這個環境而言,我使用一臺基于英偉達GeForce RTX 4090 GPU的Linux服務器,搭載24GB的VRAM。它運行Docker和英偉達容器工具包,使容器能夠訪問GPU。
我們將使用來自Hugging Face的文本生成推理服務器來運行Hermes 2 Pro。
下面的命令在端口8080上啟動推理引擎,通過REST端點為LLM提供服務。
export token="YOUR_HF_TOKEN"
export model="NousResearch/Hermes-2-Pro-Llama-3-8B"
export volume="/home/ubuntu/data"
docker run --name hermes -d --gpus all -e HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN=$token --shm-size 1g -p 8080:80 -v $volume:/data ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:2.0.3 --model-id $model --max-total-tokens 8096
To test the endpoint, run the following command:
curl 127.0.0.1:8081 \
-X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"inputs":"What is Deep Learning?"}'如果一切正常,您應該看到Hermes 2 Pro的響應。
跟蹤航班狀態的函數
在繼續下一步之前,注冊FlightAware并獲取API密鑰,使用REST API需要API密鑰。免費的個人版本足以完成本教程。
獲得API密鑰后,用Python創建以下函數,以檢索任何航班的狀態。
import ast
import json
import random
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
import requests
import pytz
def get_flight_status(flight):
"""Returns Flight Information"""
AEROAPI_BASE_URL = "https://aeroapi.flightaware.com/aeroapi"
AEROAPI_KEY="YOUR FLIGHTAWARE API KEY"
def get_api_session():
session = requests.Session()
session.headers.update({"x-apikey": AEROAPI_KEY})
return session
def fetch_flight_data(flight_id, session):
if "flight_id=" in flight_id:
flight_id = flight_id.split("flight_id=")[1]
start_date = datetime.now().date().strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
end_date = (datetime.now().date() + timedelta(days=1)).strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
api_resource = f"/flights/{flight_id}?start={start_date}&end={end_date}"
response = session.get(f"{AEROAPI_BASE_URL}{api_resource}")
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()['flights'][0]
def utc_to_local(utc_date_str, local_timezone_str):
utc_datetime = datetime.strptime(utc_date_str, '%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%SZ').replace(tzinfo=pytz.utc)
local_timezone = pytz.timezone(local_timezone_str)
local_datetime = utc_datetime.astimezone(local_timezone)
return local_datetime.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
session = get_api_session()
flight_data = fetch_flight_data(flight, session)
dep_key = 'estimated_out' if 'estimated_out' in flight_data and flight_data['estimated_out'] else \
'actual_out' if 'actual_out' in flight_data and flight_data['actual_out'] else \
'scheduled_out'
arr_key = 'estimated_in' if 'estimated_in' in flight_data and flight_data['estimated_in'] else \
'actual_in' if 'actual_in' in flight_data and flight_data['actual_in'] else \
'scheduled_in'
flight_details = {
'flight':flight,
'source': flight_data['origin']['city'],
'destination': flight_data['destination']['city'],
'depart_time': utc_to_local(flight_data[dep_key], flight_data['origin']['timezone']),
'arrival_time': utc_to_local(flight_data[arr_key], flight_data['destination']['timezone']),
'status': flight_data['status']
}
return json.dumps(flight_details)
flight_info = get_flight_status("EK524")
print(flight_info)
#'{"flight": "EK524", "source": "Dubai", "destination": "Hyderabad", "depart_time": "2024-05-23 22:00:00", "arrival_time": "2024-05-24 03:05:00", "status": "Scheduled"}'雖然代碼簡單直觀,還是讓我解釋關鍵步驟。
get_flight_status函數接受航班參數(假設是航班標識符),并以JSON格式返回格式化的航班詳細信息。它查詢AeroAPI以根據特定的航班標識符獲取航班數據,并格式化關鍵細節,比如源地、目的地、駛離時間、到達時間和狀態。
不妨看看腳本的組件:
API憑據:
AEROAPI_BASE_URL是FlightAware AeroAPI的基礎URL。
AEROAPI_KEY是用于身份驗證的API密鑰。
會話管理:
get_api_session:這個嵌套函數初始化請求。這將使用API密鑰設置所需的報頭,并返回會話對象。該會話將處理所有API請求。
數據獲取:
fetch_flight_data:這個函數接受flight_id和session作為參數。它用適當的日期過濾器構造端點URL,用于獲取一天的數據,并發送GET請求以檢索航班數據。該函數處理API響應,并提取相關的航班信息。
時間轉換:
utc_to_local:根據提供的時區字符串將UTC時間(來自API響應)轉換為本地時間。該函數幫助我們獲得基于城市的到達和駛離時間。
數據處理:
腳本根據可用的估計時間或實際時間確定駛離和到達時間的鍵,并返回到計劃時間。然后,它構造一個含有格式化航班詳細信息的字典。

上述截圖顯示了我們從FlightAware API收到的從迪拜飛往海得拉巴的阿聯酋航空EK524的響應。請注意,到達和駛離時間基于城市的當地時間。
我們旨在將該函數與Gemini 1.0 Pro集成,使其能夠實時訪問航班跟蹤信息。
將函數與Hermes 2 Pro集成
先使用以下命令安裝最新版本的Hugging Face Python SDK:
pip install --upgrade huggingface_hub導入模塊,并通過將客戶端指向TGI端點來初始化客戶端。
from huggingface_hub import InferenceClient
client = InferenceClient("http://127.0.0.1:8080")接下來,定義函數模式,采用的格式與OpenAPI函數調用的格式一樣。
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_flight_status",
"description": "Get status of a flight",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"flight": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Flight number"
}
},
"required": ["flight"]
}
}
}
]這將使用LLM用作工具的一個或多個函數填充列表。
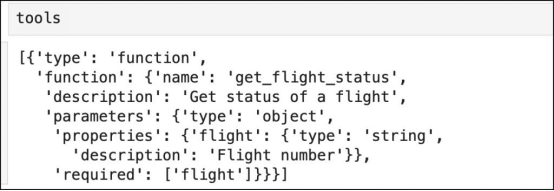
現在,我們將創建接受提示并確定是否需要調用函數的聊天機器人。如果需要調用,則LLM先返回函數名和需要調用的參數。函數的輸出作為第二次調用的一部分發送給LLM。最終的響應將根據函數的輸出得到與事實相符的正確答案。
def chatbot(prompt):
messages = [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You're a helpful assistant! Answer the users question best you can based on the tools provided. Be concise in your responses.",
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": prompt
},
]
response = client.chat_completion(messages=messages, tools=tools)
tool_calls = response.choices[0].message.tool_calls
if tool_calls:
available_functions = {
"get_flight_status": get_flight_status,
}
for tool_call in tool_calls:
function_name = tool_call.function.name
function_to_call = available_functions[function_name]
function_args = tool_call.function.arguments
function_response = function_to_call(flight=function_args.get("flight"))
messages.append(
{
"role": "tool",
"name": function_name,
"content": function_response
}
)
final_response = client.chat_completion(messages=messages)
return final_response
return response目標LLM期望的提示的自動格式化是使用Hugging Face Python庫的一個好處。比如說,使用函數時,Hermes 2 Pro的提示需要按照特定的格式進行結構化:
<|im_start|>system
You are a function calling AI model. You are provided with function signatures within XML tags. You may call one or more functions to assist with the user query. Don't make assumptions about what values to plug into functions. Here are the available tools: [{'type': 'function', 'function': {'name': 'get_stock_fundamentals', 'description': 'Get fundamental data for a given stock symbol using yfinance API.', 'parameters': {'type': 'object', 'properties': {'symbol': {'type': 'string'}}, 'required': ['symbol']}}}] Use the following pydantic model json schema for each tool call you will make: {'title': 'FunctionCall', 'type': 'object', 'properties': {'arguments': {'title': 'Arguments', 'type': 'object'}, 'name': {'title': 'Name', 'type': 'string'}}, 'required':
['arguments', 'name']} For each function call return a json object with function name and arguments within XML tags as follows:
{'arguments': , 'name': }
<|im_end|>同樣,函數的輸出可以以以下格式發送到LLM:
<|im_start|>tool
{"name": "get_stock_fundamentals", "content": {'symbol': 'TSLA', 'company_name': 'Tesla, Inc.', 'sector': 'Consumer Cyclical', 'industry': 'Auto Manufacturers', 'market_cap': 611384164352, 'pe_ratio': 49.604652, 'pb_ratio': 9.762013, 'dividend_yield': None, 'eps': 4.3, 'beta': 2.427, '52_week_high': 299.29, '52_week_low': 152.37}}
<|im_end|>確保提示遵循該模板需要仔細格式化。InferenceClient類可高效地處理這種轉換,使開發人員能夠在提示中使用系統、用戶、工具和助手角色的熟悉的OpenAI格式。
在首次調用聊天完成API時,LLM給出以下答案作為響應:

隨后,在調用函數之后,我們將結果嵌入到消息中并將其發回給LLM。
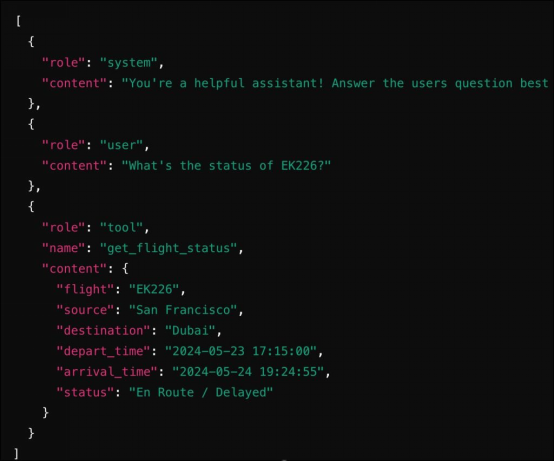
正如您所見,集成函數調用的工作流程與OpenAI非常相似。
現在是時候調用聊天機器人并通過提示來測試它了。
res=chatbot("What's the status of EK226?")
print(res.choices[0].message.content)聊天機器人的完整代碼如下所示。
from huggingface_hub import InferenceClient
client = InferenceClient("http://127.0.0.1:8080")
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_flight_status",
"description": "Get status of a flight",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"flight": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Flight number"
}
},
"required": ["flight"]
}
}
}
]
def chatbot(prompt):
messages = [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You're a helpful assistant! Answer the users question best you can based on the tools provided. Be concise in your responses.",
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": prompt
},
]
response = client.chat_completion(messages=messages, tools=tools)
tool_calls = response.choices[0].message.tool_calls
if tool_calls:
available_functions = {
"get_flight_status": get_flight_status,
}
for tool_call in tool_calls:
function_name = tool_call.function.name
function_to_call = available_functions[function_name]
function_args = tool_call.function.arguments
function_response = function_to_call(flight=function_args.get("flight"))
messages.append(
{
"role": "tool",
"name": function_name,
"content": function_response
}
)
final_response = client.chat_completion(messages=messages)
return final_response
return response
res=chatbot("What's the status of EK226?")
print(res.choices[0].message.content) 原文標題:Building an Open LLM App Using Hermes 2 Pro Deployed Locally,作者:Janakiram MSV

































