淺析細胞圖像數(shù)據(jù)的主動學習
通過細胞圖像的標簽對模型性能的影響,為數(shù)據(jù)設置優(yōu)先級和權重。
許多機器學習任務的主要障礙之一是缺乏標記數(shù)據(jù)。而標記數(shù)據(jù)可能會耗費很長的時間,并且很昂貴,因此很多時候嘗試使用機器學習方法來解決問題是不合理的。
為了解決這個問題,機器學習領域出現(xiàn)了一個叫做主動學習的領域。主動學習是機器學習中的一種方法,它提供了一個框架,根據(jù)模型已經(jīng)看到的標記數(shù)據(jù)對未標記的數(shù)據(jù)樣本進行優(yōu)先排序。如果想
細胞成像的分割和分類等技術是一個快速發(fā)展的領域研究。就像在其他機器學習領域一樣,數(shù)據(jù)的標注是非常昂貴的,并且對于數(shù)據(jù)標注的質(zhì)量要求也非常的高。針對這一問題,本篇文章介紹一種對紅細胞和白細胞圖像分類任務的主動學習端到端工作流程。
我們的目標是將生物學和主動學習的結合,并幫助其他人使用主動學習方法解決生物學領域中類似的和更復雜的任務。
本篇文主要由三個部分組成:
- 細胞圖像預處理——在這里將介紹如何預處理未分割的血細胞圖像。
- 使用CellProfiler提取細胞特征——展示如何從生物細胞照片圖像中提取形態(tài)學特征,以用作機器學習模型的特征。
- 使用主動學習——展示一個模擬使用主動學習和不使用主動學習的對比實驗。
細胞圖像預處理
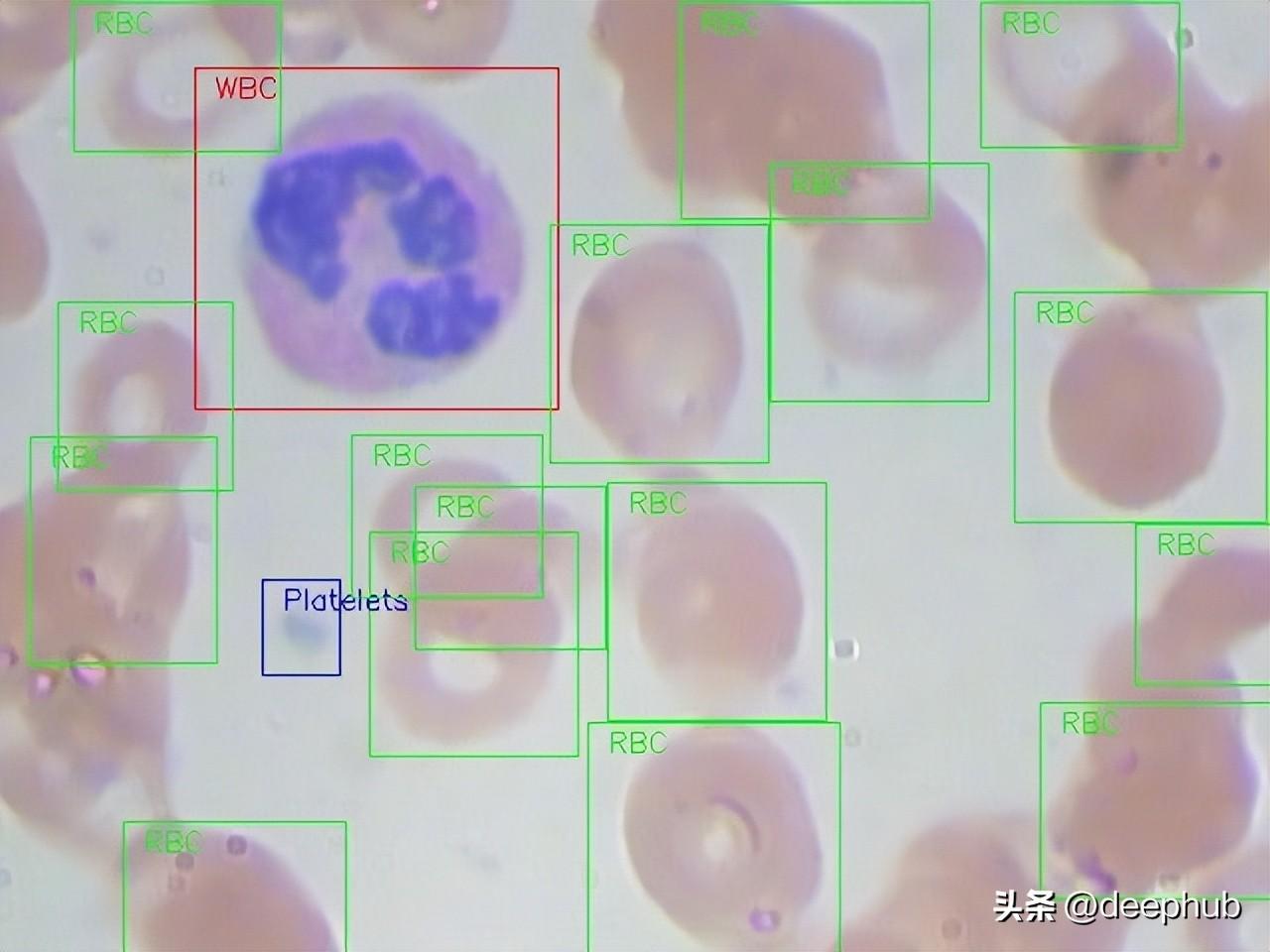
我們將使用在MIT許可的血細胞圖像數(shù)據(jù)集(GitHub和Kaggle)。每張圖片都根據(jù)紅細胞(RBC)和白細胞(WBC)分類進行標記。對于這4種白細胞(嗜酸性粒細胞、淋巴細胞、單核細胞和中性粒細胞)還有附加的標簽,但在本文的研究中沒有使用這些標簽。
下面是一個來自數(shù)據(jù)集的全尺寸原始圖像的例子:
創(chuàng)建樣本DF
原始數(shù)據(jù)集包含一個export.py腳本,它將XML注釋解析為一個CSV表,其中包含每個細胞的文件名、細胞類型標簽和邊界框。
原始腳本沒有包含cell_id列,但我們要對單個細胞進行分類,所以我們稍微修改了代碼,添加了該列并添加了一列包括image_id和cell_id的filename列:
import os, sys, randomimport xml.etree.ElementTree as ETfrom glob import globimport pandas as pdfrom shutil import copyfileannotations = glob('BCCD_Dataset/BCCD/Annotations/*.xml')df = []for file in annotations:#filename = file.split('/')[-1].split('.')[0] + '.jpg'#filename = str(cnt) + '.jpg'filename = file.split('\\')[-1]filename =filename.split('.')[0] + '.jpg'row = []parsedXML = ET.parse(file)cell_id = 0for node in parsedXML.getroot().iter('object'):blood_cells = node.find('name').textxmin = int(node.find('bndbox/xmin').text)xmax = int(node.find('bndbox/xmax').text)ymin = int(node.find('bndbox/ymin').text)ymax = int(node.find('bndbox/ymax').text)row = [filename, cell_id, blood_cells, xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax]df.append(row)cell_id += 1data = pd.DataFrame(df, columns=['filename', 'cell_id', 'cell_type', 'xmin', 'xmax', 'ymin', 'ymax'])data['image_id'] = data['filename'].apply(lambda x: int(x[-7:-4]))data[['filename', 'image_id', 'cell_id', 'cell_type', 'xmin', 'xmax', 'ymin', 'ymax']].to_csv('bccd.csv', index=False)裁剪
為了能夠處理數(shù)據(jù),第一步是根據(jù)邊界框坐標裁剪全尺寸圖像。這就產(chǎn)生了很多大小不一的細胞圖像:

裁剪的代碼如下:
import osimport pandas as pdfrom PIL import Imagedef crop_cell(row):"""crop_cell(row)given a pd.Series row of the dataframe, load row['filename'] with PIL,crop it to the box row['xmin'], row['xmax'], row['ymin'], row['ymax']save the cropped image,return cropped filename"""input_dir = 'BCCD\JPEGImages'output_dir = 'BCCD\cropped'# open imageim = Image.open(f"{input_dir}\{row['filename']}")# size of the image in pixelswidth, height = im.size# setting the points for cropped imageleft = row['xmin']bottom = row['ymax']right = row['xmax']top = row['ymin']# cropped imageim1 = im.crop((left, top, right, bottom))cropped_fname = f"BloodImage_{row['image_id']:03d}_{row['cell_id']:02d}.jpg"# shows the image in image viewer# im1.show()# save imagetry:im1.save(f"{output_dir}\{cropped_fname}")except:return 'error while saving image'return cropped_fnameif __name__ == "__main__":# load labels csv into Pandas DataFramefilepath = "BCCD\dataset2-master\labels.csv"df = pd.read_csv(filepath)# iterate through cells, crop each cell, and save cropped cell to filedataset_df['cell_filename'] = dataset_df.apply(crop_cell, axis=1)以上就是我們所做的所有預處理操作。現(xiàn)在,我們繼續(xù)使用CellProfiler提取特征。
使用CellProfiler提取細胞特征
CellProfiler是一個免費的開源圖像分析軟件,可以從大規(guī)模細胞圖像中自動定量測量。CellProfiler還包含一個GUI界面,允許我們可視化的操作
首先下載CellProfiler,如果CellProfiler無法打開,則可能需要安裝Visual C ++發(fā)布包,具體安裝方式參考官網(wǎng)。
打開軟件就可以加載圖像了, 如果想構建管道可以在CellProfiler官網(wǎng)找到其提供的可用的功能列表。 大多數(shù)功能分為三個主要組:圖像處理,目標的處理和測量。
常用的功能如下:
圖像處理 - 轉(zhuǎn)為灰度圖:
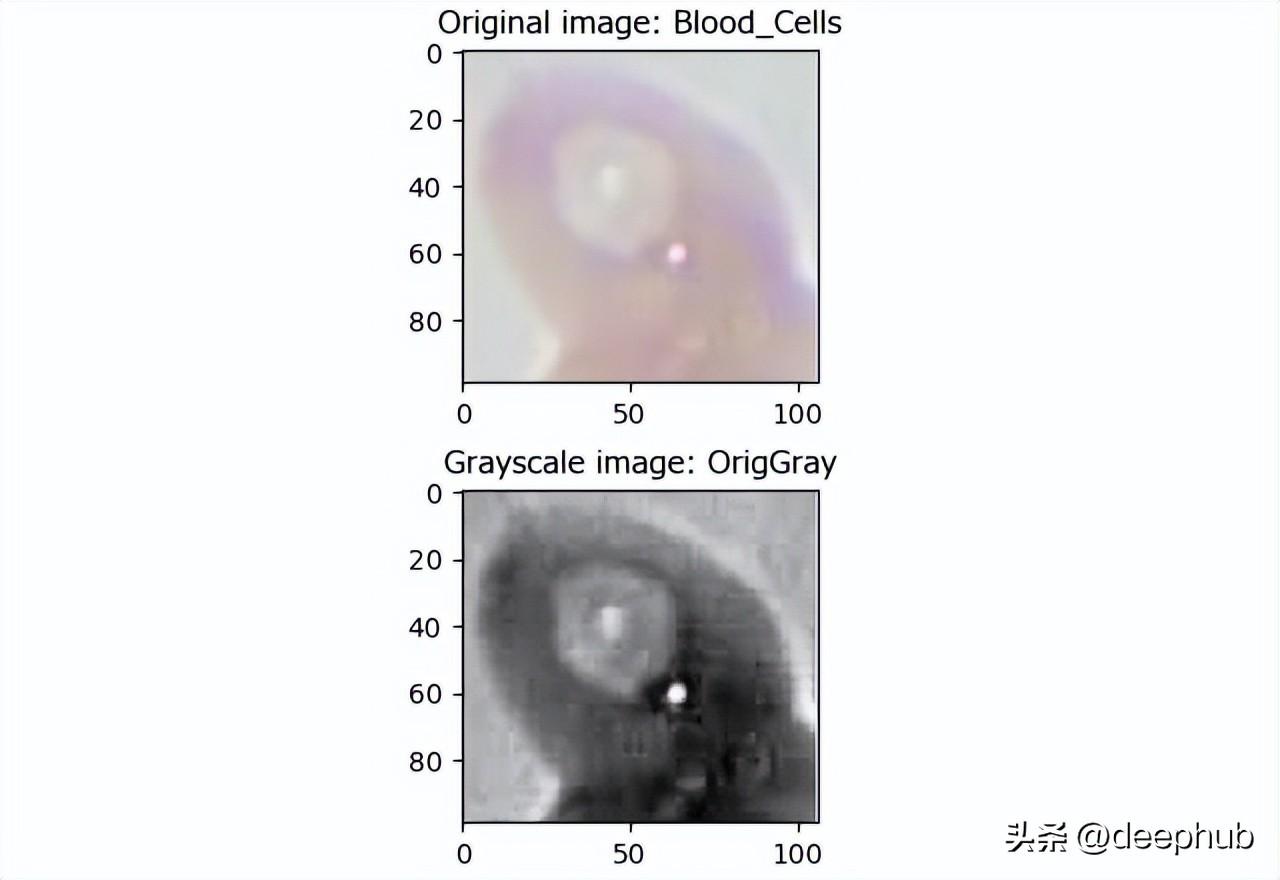
對象目標處理 - 識別主要對象
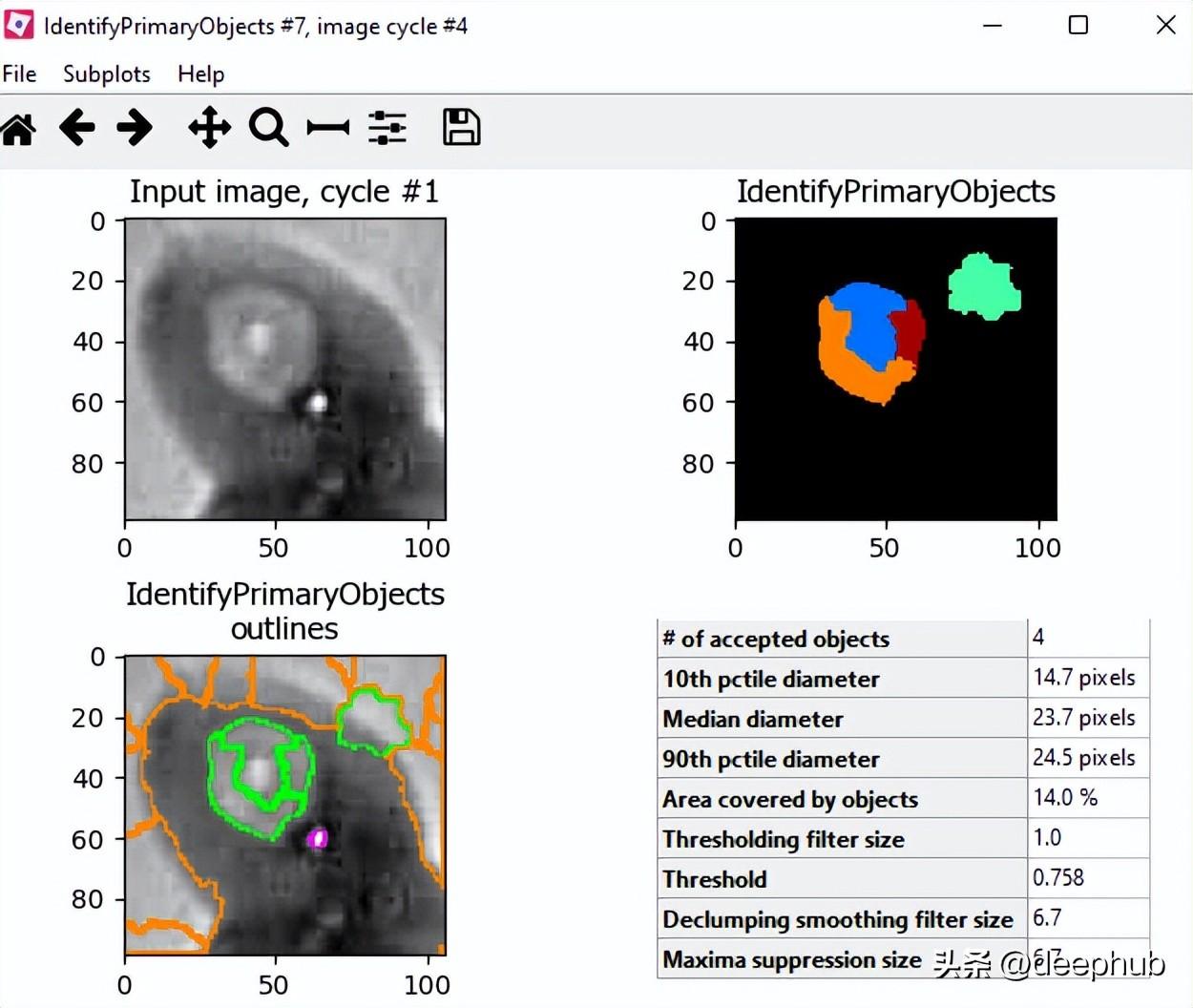
測量 - 測量對象強度
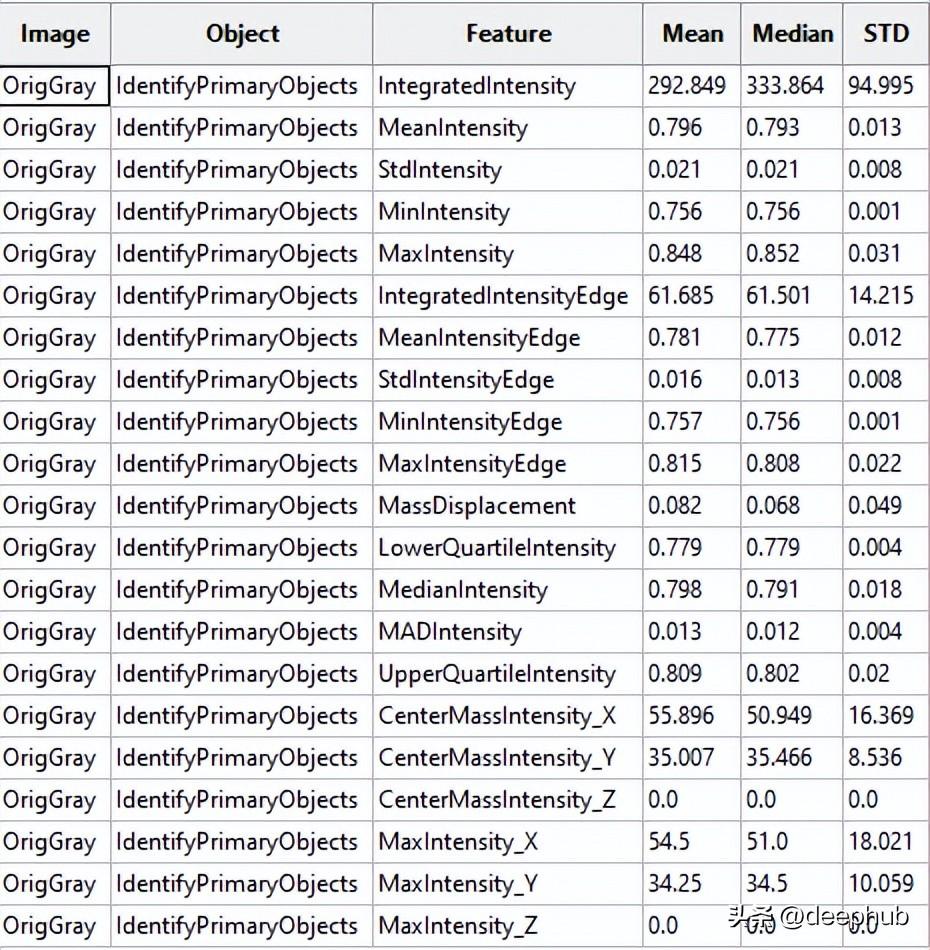
CellProfiler可以將輸出為CSV文件或者保存指定數(shù)據(jù)庫中。這里我們將輸出保存為CSV文件,然后將其加載到Python進行進一步處理。
說明:CellProfiler還可以將你處理圖像的流程保存并進行分享。
主動學習
我們現(xiàn)在已經(jīng)有了訓練需要的搜有數(shù)據(jù),現(xiàn)在可以開始試驗使用主動學習策略是否可以通過更少的數(shù)據(jù)標記獲得更高的準確性。 我們的假設是:使用主動學習可以通過大量減少在細胞分類任務上訓練機器學習模型所需的標記數(shù)據(jù)量來節(jié)省寶貴的時間和精力。
主動學習框架
在深入研究實驗之前,我們希望對modAL進行快速介紹: modAL是Python的活躍學習框架。 它提供了Sklearn API,因此可以非常容易的將其集成到代碼中。 該框架可以輕松地使用不同的主動學習策略。 他們的文檔也很清晰,所以建議從它開始你的一個主動學習項目。
主動學習與隨機學習
為了驗證假設,我們將進行一項實驗,將添加新標簽數(shù)據(jù)的隨機子抽樣策略與主動學習策略進行比較。開始用一些相同的標記樣本訓練2個Logistic回歸估計器。然后將在一個模型中使用隨機策略,在第二個模型中使用主動學習策略。
我們首先為實驗準備數(shù)據(jù),加載由Cell Profiler言創(chuàng)建的特征。 這里過濾了無色血細胞的血小板,只保留紅和白細胞(將問題簡化,并減少數(shù)據(jù)量) 。所以現(xiàn)在我們正在嘗試解決二進制分類問題 - RBC與WBC。使用Sklearn Label的label encoder進行編碼,并拆分數(shù)據(jù)集進行訓練和測試。
# imports for the whole experimentimport numpy as npfrom matplotlib import pyplot as pltfrom modAL import ActiveLearnerimport pandas as pdfrom modAL.uncertainty import uncertainty_samplingfrom sklearn import preprocessingfrom sklearn.metrics import , average_precision_scorefrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression# upload the cell profiler features for each celldata = pd.read_csv('Zaretski_Image_All.csv')# filter plateletsdata = data[data['cell_type'] != 'Platelets']# define the labeltarget = 'cell_type'label_encoder = preprocessing.LabelEncoder()y = label_encoder.fit_transform(data[target])# take the learning features onlyX = data.iloc[:, 5:]# create training and testing setsX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X.to_numpy(), y, test_size=0.33, random_state=42)下一步就是創(chuàng)建模型
dummy_learner = LogisticRegression()
active_learner = ActiveLearner(
estimator=LogisticRegression(),
query_strategy=uncertainty_sampling()
)
dummy_learner是使用隨機策略的模型,而active_learner是使用主動學習策略的模型。為了實例化一個主動學習模型,我們使用modAL包中的ActiveLearner對象。在“estimator”字段中,可以插入任何sklearnAPI兼容的模型。在query_strategy '字段中可以選擇特定的主動學習策略。這里使用“uncertainty_sampling()”。這方面更多的信息請查看modAL文檔。
將訓練數(shù)據(jù)分成兩組。第一個是訓練數(shù)據(jù),我們知道它的標簽,會用它來訓練模型。第二個是驗證數(shù)據(jù),雖然標簽也是已知的,但是我們假裝不知道它的標簽,并通過模型預測的標簽和實際標簽進行比較來評估模型的性能。然后我們將訓練的數(shù)據(jù)樣本數(shù)設置成5。
# the training size that we will start withbase_size = 5# the 'base' data that will be the training set for our modelX_train_base_dummy = X_train[:base_size]X_train_base_active = X_train[:base_size]y_train_base_dummy = y_train[:base_size]y_train_base_active = y_train[:base_size]# the 'new' data that will simulate unlabeled data that we pick a sample from and label itX_train_new_dummy = X_train[base_size:]X_train_new_active = X_train[base_size:]y_train_new_dummy = y_train[base_size:]y_train_new_active = y_train[base_size:]
我們訓練298個epoch,在每個epoch中,將訓練這倆個模型和選擇下一個樣本,并根據(jù)每個模型的策略選擇是否將樣本加入到我們的“基礎”數(shù)據(jù)中,并在每個epoch中測試其準確性。因為分類是不平衡的,所以使用平均精度評分來衡量模型的性能。
在隨機策略中選擇下一個樣本,只需將下一個樣本添加到虛擬數(shù)據(jù)集的“新”組中,這是因為數(shù)據(jù)集已經(jīng)是打亂的的,因此不需要在進行這個操作。對于主動學習,將使用名為“query”的ActiveLearner方法,該方法獲取“新”組的未標記數(shù)據(jù),并返回他建議添加到訓練“基礎”組的樣本索引。被選擇的樣本都將從組中刪除,因此樣本只能被選擇一次。
# arrays to accumulate the scores of each simulation along the epochsdummy_scores = []active_scores = []# number of desired epochsrange_epoch = 298# running the experimentfor i in range(range_epoch):# train the models on the 'base' datasetactive_learner.fit(X_train_base_active, y_train_base_active)dummy_learner.fit(X_train_base_dummy, y_train_base_dummy)# evaluate the modelsdummy_pred = dummy_learner.predict(X_test)active_pred = active_learner.predict(X_test)# accumulate the scoresdummy_scores.append(average_precision_score(dummy_pred, y_test))active_scores.append(average_precision_score(active_pred, y_test))# pick the next sample in the random strategy and randomly# add it to the 'base' dataset of the dummy learner and remove it from the 'new' datasetX_train_base_dummy = np.append(X_train_base_dummy, [X_train_new_dummy[0, :]], axis=0)y_train_base_dummy = np.concatenate([y_train_base_dummy, np.array([y_train_new_dummy[0]])], axis=0)X_train_new_dummy = X_train_new_dummy[1:]y_train_new_dummy = y_train_new_dummy[1:]# pick next sample in the active strategyquery_idx, query_sample = active_learner.query(X_train_new_active)# add the index to the 'base' dataset of the active learner and remove it from the 'new' datasetX_train_base_active = np.append(X_train_base_active, X_train_new_active[query_idx], axis=0)y_train_base_active = np.concatenate([y_train_base_active, y_train_new_active[query_idx]], axis=0)X_train_new_active = np.concatenate([X_train_new_active[:query_idx[0]], X_train_new_active[query_idx[0] + 1:]], axis=0)y_train_new_active = np.concatenate([y_train_new_active[:query_idx[0]], y_train_new_active[query_idx[0] + 1:]], axis=0)
結果如下:
plt.plot(list(range(range_epoch)), active_scores, label='Active Learning')plt.plot(list(range(range_epoch)), dummy_scores, label='Dummy')plt.xlabel('number of added samples')plt.ylabel('average precision score')plt.legend(loc='lower right')plt.savefig("models robustness vs dummy.png", bbox_inches='tight')plt.show()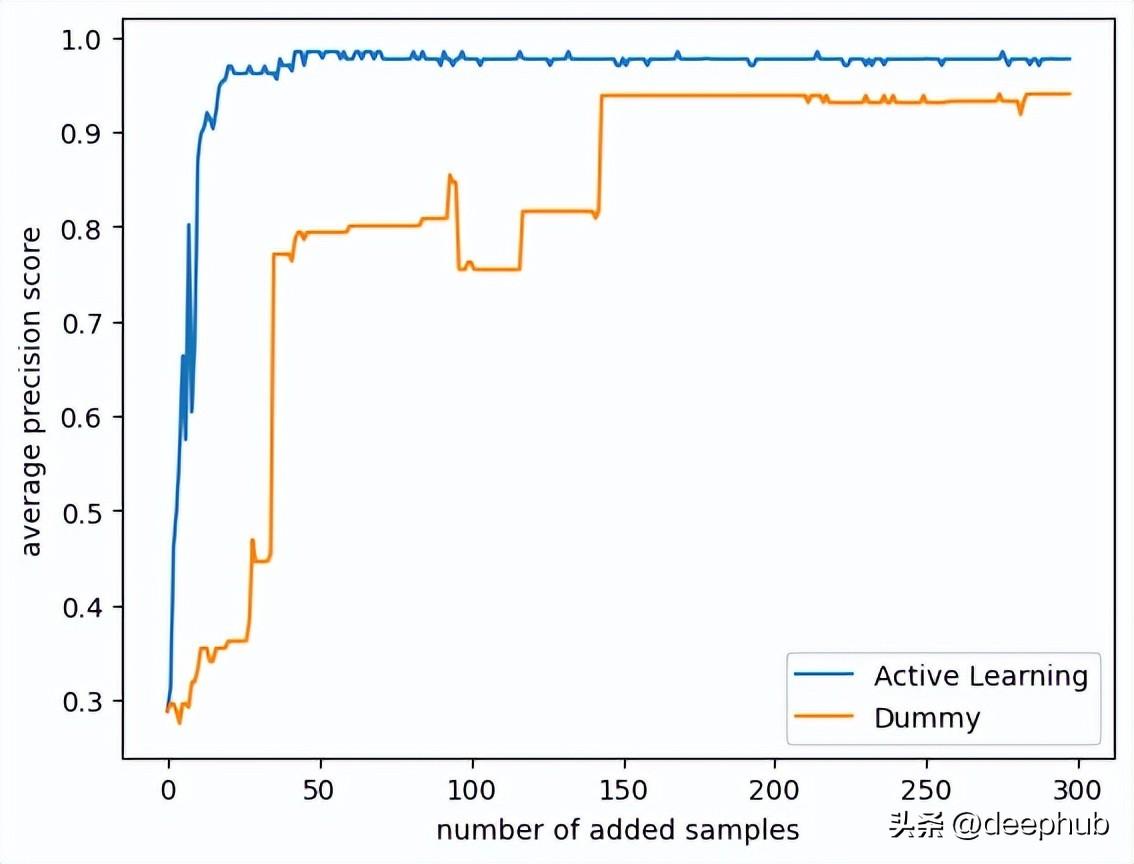
策略之間的差異還是很大的,可以看到主動學習只使用25個樣本就可以達到平均精度0.9得分! 而使用隨機的策略則需要175個樣本才能達到相同的精度!
此外主動學習策略的模型的分數(shù)接近0.99,而隨機模型的分數(shù)在0.95左右停止了! 如果我們使用所有數(shù)據(jù),那么它們最終分數(shù)是相同的,但是我們的研究目的是在少量標注數(shù)據(jù)的前提下訓練,所以只使用了數(shù)據(jù)集中的300個隨機樣本。
總結
本文展示了將主動學習用于細胞成像任務的好處。主動學習是機器學習中的一組方法,可根據(jù)其標簽對模型性能的影響來優(yōu)先考慮未標記的數(shù)據(jù)示例的解決方案。由于標記數(shù)據(jù)是一項涉及許多資源(金錢和時間)的任務,因此判斷那些標記那些樣本可以最大程度地提高模型的性能是非常必要的。
細胞成像為生物學,醫(yī)學和藥理學領域做出了巨大貢獻。以前分析細胞圖像需要有價值的專業(yè)人力資本,但是像主動學習這種技術的出現(xiàn)為醫(yī)學領域這種需要大量人力標注數(shù)據(jù)集的領域提供了一個非常好的解決方案。