設(shè)計(jì)模式系列—橋接模式
本篇和大家一起來學(xué)習(xí)橋接模式相關(guān)內(nèi)容。
模式定義
將抽象與實(shí)現(xiàn)分離,使它們可以獨(dú)立變化。它是用組合關(guān)系代替繼承關(guān)系來實(shí)現(xiàn),從而降低了抽象和實(shí)現(xiàn)這兩個(gè)可變維度的耦合度。
模式實(shí)現(xiàn)如下:
- package com.niuh.designpattern.bridge.v1;
- /**
- * 橋接模式
- */
- public class BridgePattern {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Implementor imple=new ConcreteImplementorA();
- Abstraction abs=new RefinedAbstraction(imple);
- abs.Operation();
- }
- }
- //實(shí)現(xiàn)化角色
- interface Implementor {
- void OperationImpl();
- }
- //具體實(shí)現(xiàn)化角色
- class ConcreteImplementorA implements Implementor {
- public void OperationImpl() {
- System.out.println("具體實(shí)現(xiàn)化(Concrete Implementor)角色被訪問");
- }
- }
- //抽象化角色
- abstract class Abstraction {
- protected Implementor imple;
- protected Abstraction(Implementor imple) {
- this.imple = imple;
- }
- public abstract void Operation();
- }
- //擴(kuò)展抽象化角色
- class RefinedAbstraction extends Abstraction {
- protected RefinedAbstraction(Implementor imple) {
- super(imple);
- }
- public void Operation() {
- System.out.println("擴(kuò)展抽象化(Refined Abstraction)角色被訪問");
- imple.OperationImpl();
- }
- }
輸出結(jié)果如下:
- 擴(kuò)展抽象化(Refined Abstraction)角色被訪問
- 具體實(shí)現(xiàn)化(Concrete Implementor)角色被訪問
解決的問題
在有多種可能會變化的情況下,用繼承會造成類爆炸問題,擴(kuò)展起來不靈活。
模式組成
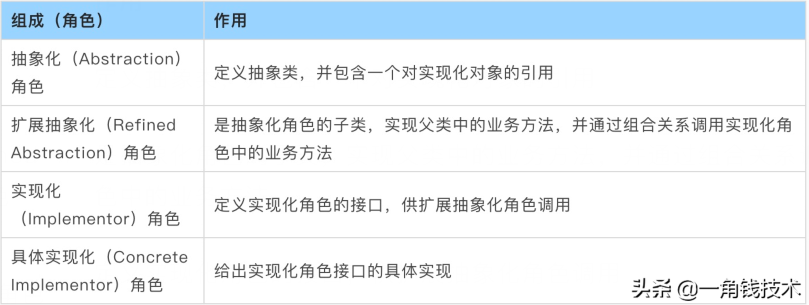
可以將抽象化部分與實(shí)現(xiàn)化部分分開,取消二者的繼承關(guān)系,改用組合關(guān)系。
實(shí)例說明
實(shí)例概況
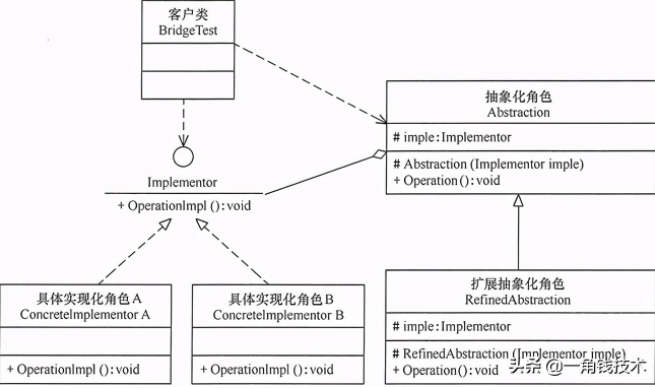
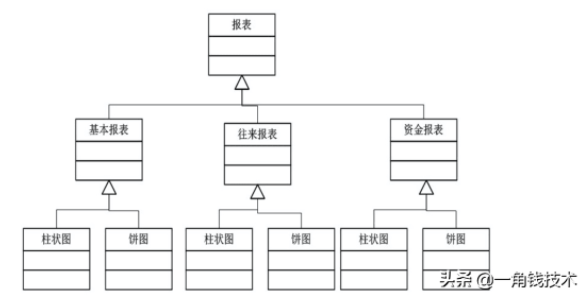
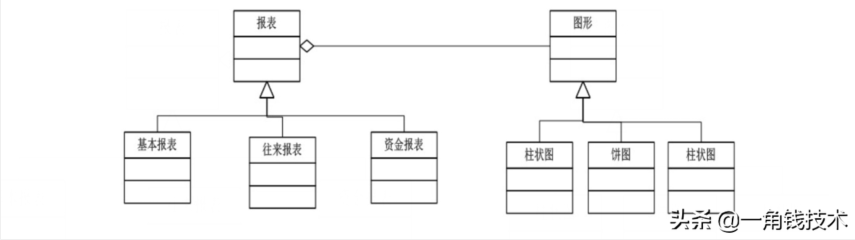
某公司開發(fā)了一個(gè)財(cái)務(wù)管理系統(tǒng),其中有個(gè)報(bào)表生成器的工具模塊,客戶可以指定任意一種報(bào)表類型,如基本報(bào)表,往來報(bào)表,資金報(bào)表,資產(chǎn)報(bào)表等,并且可以指定不同 的報(bào)表樣式,如餅圖,柱狀圖等。系統(tǒng)設(shè)計(jì)人員針對這個(gè)報(bào)表生成器的結(jié)構(gòu)設(shè)計(jì)了如下圖所示的類圖。
后來在客戶使用過程中,客戶又希望增加一個(gè)新的報(bào)表和新的線形圖,開發(fā)人員這個(gè)時(shí)候發(fā)現(xiàn)維護(hù)起來非常麻煩,設(shè)計(jì)人員經(jīng)過仔細(xì)分析,發(fā)現(xiàn)存在嚴(yán)重的問題,因?yàn)樾略黾右粋€(gè)報(bào)表或者圖,需要增加很多子類。所以,系統(tǒng)分析師最終對這個(gè)模塊根據(jù)面向?qū)ο蟮脑O(shè)計(jì)原則對上面的方案進(jìn)行了重構(gòu),重構(gòu)后的圖如下所示。
在本重構(gòu)方案中,將報(bào)表和圖形設(shè)計(jì)成兩個(gè)繼承結(jié)構(gòu),兩者都可以獨(dú)立變化,編程的時(shí)候可以只針對抽象類編碼,而在運(yùn)行的時(shí)候再將具體的圖形子類對象注入到具體的 報(bào)表類中。這樣的話,系統(tǒng)就具有良好的可擴(kuò)展性和可維護(hù)性,并且滿足了面向?qū)ο笤O(shè)計(jì)原則的開閉原則。
使用步驟
步驟1:定義實(shí)現(xiàn)化角色,報(bào)表接口
- interface IReport {
- void operationImpl();
- }
步驟2:定義具體實(shí)現(xiàn)化角色(基本報(bào)表、往來報(bào)表、資金報(bào)表)
- class BasicReport implements IReport {
- @Override
- public void operationImpl() {
- System.out.println("基本報(bào)表被訪問.");
- }
- }
- class IntercourseReport implements IReport {
- @Override
- public void operationImpl() {
- System.out.println("往來報(bào)表被訪問.");
- }
- }
- class CapitalReport implements IReport {
- @Override
- public void operationImpl() {
- System.out.println("資金報(bào)表被訪問.");
- }
- }
步驟3:定義抽象化角色,圖形
- abstract class AbstractionGraph {
- protected IReport iReport;
- public AbstractionGraph(IReport iReport) {
- this.iReport = iReport;
- }
- abstract void operation();
- }
步驟4:定義擴(kuò)展抽象化角色(柱狀圖、餅圖)
- class Barchart extends AbstractionGraph {
- public Barchart(IReport iReport) {
- super(iReport);
- }
- @Override
- void operation() {
- System.out.println("柱狀圖被訪問.");
- iReport.operationImpl();
- }
- }
- class Piechart extends AbstractionGraph {
- public Piechart(IReport iReport) {
- super(iReport);
- }
- @Override
- void operation() {
- System.out.println("餅圖被訪問.");
- iReport.operationImpl();
- }
- }
步驟5:測試
- public class BridgePattern {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //實(shí)現(xiàn)化和抽象化分離
- // 基本報(bào)表
- IReport basicReport = new BasicReport();
- // 往來報(bào)表
- IReport intercourseReport = new IntercourseReport();
- // 資金報(bào)表
- IReport capitalReport = new CapitalReport();
- // 基本報(bào)表使用柱狀圖
- AbstractionGraph barchart = new Barchart(basicReport);
- barchart.operation();
- // 基本報(bào)表使用餅圖
- AbstractionGraph piechart = new Piechart(basicReport);
- piechart.operation();
- }
- }
輸出結(jié)果
- 柱狀圖被訪問.
- 基本報(bào)表被訪問.
- 餅圖被訪問.
- 基本報(bào)表被訪問.
優(yōu)點(diǎn)
橋接模式遵循了里氏替換原則和依賴倒置原則,最終實(shí)現(xiàn)了開閉原則,對修改關(guān)閉,對擴(kuò)展開放。這里將橋接模式的優(yōu)缺點(diǎn)總結(jié)如下。
橋接(Bridge)模式的優(yōu)點(diǎn):
- 抽象與實(shí)現(xiàn)分離,擴(kuò)展能力強(qiáng)
- 符合開閉原則
- 符合合成復(fù)用原則
- 其實(shí)現(xiàn)細(xì)節(jié)對客戶透明
缺點(diǎn)
由于聚合關(guān)系建立在抽象層,要求開發(fā)者針對抽象化進(jìn)行設(shè)計(jì)與編程,能正確地識別出系統(tǒng)中兩個(gè)獨(dú)立變化的維度,這增加了系統(tǒng)的理解與設(shè)計(jì)難度。
應(yīng)用場景
當(dāng)一個(gè)類內(nèi)部具備兩種或多種變化維度時(shí),使用橋接模式可以解耦這些變化的維度,使高層代碼架構(gòu)穩(wěn)定。
橋接模式通常適用于以下場景:
- 當(dāng)一個(gè)類存在兩個(gè)獨(dú)立變化的維度,且這兩個(gè)維度都需要進(jìn)行擴(kuò)展時(shí);
- 當(dāng)一個(gè)系統(tǒng)不希望使用繼承或因?yàn)槎鄬哟卫^承導(dǎo)致系統(tǒng)類的個(gè)數(shù)急劇增加時(shí);
- 當(dāng)一個(gè)系統(tǒng)需要在構(gòu)件的抽象化角色和具體化角色之間增加更多的靈活性時(shí)。
橋接模式的一個(gè)常見使用場景就是替換繼承。我們知道,繼承擁有很多優(yōu)點(diǎn),比如,抽象、封裝、多態(tài)等,父類封裝共性,子類實(shí)現(xiàn)特性。繼承可以很好的實(shí)現(xiàn)代碼復(fù)用(封裝)的功能,但這也是繼承的一大缺點(diǎn)。
因?yàn)楦割悡碛械姆椒ǎ宇愐矔^承得到,無論子類需不需要,這說明繼承具備強(qiáng)侵入性(父類代碼侵入子類),同時(shí)會導(dǎo)致子類臃腫。因此,在設(shè)計(jì)模式中,有一個(gè)原則為優(yōu)先使用組合/聚合,而不是繼承。
橋接模式模式的擴(kuò)展
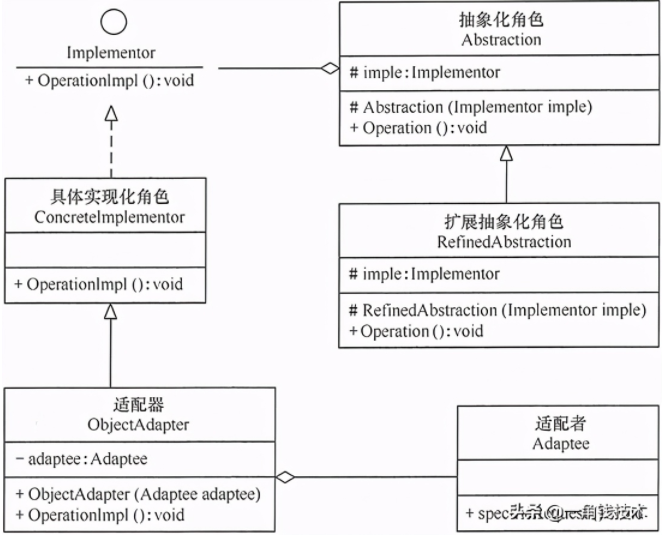
在軟件開發(fā)中,有時(shí)橋接(Bridge)模式可與適配器模式聯(lián)合使用。當(dāng)橋接(Bridge)模式的實(shí)現(xiàn)化角色的接口與現(xiàn)有類的接口不一致時(shí),可以在二者中間定義一個(gè)適配器將二者連接起來,其結(jié)構(gòu)圖如下:
源碼中的應(yīng)用
- JDBC驅(qū)動程序
- ......
DriverManager類
DriverManager作為一個(gè)抽象化角色,聚合了實(shí)現(xiàn)化角色Connection,只不過與標(biāo)準(zhǔn)的橋梁模式不一樣的是,DriverManager類下面沒有子類。
- // Worker method called by the public getConnection() methods.
- private static Connection getConnection(
- String url, java.util.Properties info, Class<?> caller) throws SQLException {
- /*
- * When callerCl is null, we should check the application's
- * (which is invoking this class indirectly)
- * classloader, so that the JDBC driver class outside rt.jar
- * can be loaded from here.
- */
- ClassLoader callerCL = caller != null ? caller.getClassLoader() : null;
- synchronized(DriverManager.class) {
- // synchronize loading of the correct classloader.
- if (callerCL == null) {
- callerCL = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
- }
- }
- if(url == null) {
- throw new SQLException("The url cannot be null", "08001");
- }
- println("DriverManager.getConnection(\"" + url + "\")");
- // Walk through the loaded registeredDrivers attempting to make a connection.
- // Remember the first exception that gets raised so we can reraise it.
- SQLException reason = null;
- for(DriverInfo aDriver : registeredDrivers) {
- // If the caller does not have permission to load the driver then
- // skip it.
- if(isDriverAllowed(aDriver.driver, callerCL)) {
- try {
- println(" trying " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName());
- Connection con = aDriver.driver.connect(url, info);
- if (con != null) {
- // Success!
- println("getConnection returning " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName());
- return (con);
- }
- } catch (SQLException ex) {
- if (reason == null) {
- reason = ex;
- }
- }
- } else {
- println(" skipping: " + aDriver.getClass().getName());
- }
- }
- // if we got here nobody could connect.
- if (reason != null) {
- println("getConnection failed: " + reason);
- throw reason;
- }
- println("getConnection: no suitable driver found for "+ url);
- throw new SQLException("No suitable driver found for "+ url, "08001");
- }
PS:以上代碼提交在 Github :
https://github.com/Niuh-Study/niuh-designpatterns.git