一文帶你掌握ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner如何使用及實現原理
1.概述
ApplicationRunner 和 CommandLineRunner 是 Spring Boot 提供的兩個接口,允許在 Spring 應用程序啟動完成后執行特定的代碼。它們的主要作用是在應用啟動后執行一段初始化或任務邏輯,常見于一些啟動任務,例如加載數據、驗證配置、執行調度等。接下來我們就來詳細看看它們在項目開發中的實際應用
2.實際應用
這兩個擴展點在實際開發中的應用場景挺廣泛的,下面就來看看幾個常見的。
2.1 服務啟動后數據初始化
在應用啟動時加載初始化數據,如將初始數據加載到數據庫、從文件讀取數據、緩存熱點數據等。可以在 CommandLineRunner 或 ApplicationRunner 中執行這些初始化邏輯,確保在應用服務正式對外提供服務之前,必要的數據已經準備好。
這個應用場景我深有感觸,因為這種應用操作可以“去運維化”,尤其對于系統是新安裝或部署而言,它確保應用程序所需的上下文數據無誤,可以立即開始運行,而無需通過手動干預來插入基本數據(PS:環境基礎數據靠運維部署時候去插入總是不可靠的......)。本著天助自助者的原則,我們可以通過CommandLineRunner來完成項目服務環境初始化的工作,這里以平時的后臺管理系統來講述一下,大部分的后臺系統都是基于RBAC模型(Role-Based Access Control:基于角色的訪問控制)進行授權和認證的,這就意味著我們一個全新系統部署之后,會默認插入一個超管賬號,他可以登陸系統訪問所有功能,比如說他可以新增員工,給新員工賦予權限等等,這樣系統就可以用起來了。
@Component
public class DataInitializer implements CommandLineRunner {
@Resource
private EnvInitMapper envInitMapper;
@Resource
private UserService userService;
@Resource
private RoleService roleService;
@Resource
private UserRoleService userRoleService;
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
// 1/判斷是不是第一次啟動 若是,執行初始數據插入等操作 若不是,不執行
// 這個可以讀取數據庫標志,初始化之后插入一個標志記錄即可, 當然也可以讀取緩存
QueryWrapper<EnvInit>queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
EnvInit init = envInitMapper.selectOne(queryWrapper);
if (Objects.isNull(init)) {
// 2.第一次初始化環境
userService.firstInitData();
// 3.插入已經初始化標志
init = new EnvInit();
init.setIsInit(1);
envInitMapper.insert(init);
}
}
/**
* 初始化環境基礎數據,可以插入環境所需的任何數據
*/
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void initData() {
userService.firstInitData();
roleService.firstInitData();
userRoleService.firstInitData();
}
}這里我們只是舉例插入了菜單權限所需的基礎數據,你可以根據自身服務環境需求插入所需的任何基礎數據,以保證系統能夠順利正常運行。我們還判斷了是不是第一次初始化基礎數據,防止每次系統服務重啟之后重復插入。
2.2 應用啟動時加載配置信息
在某些情況下,應用可能需要在啟動時加載外部配置信息或數據庫中的參數到內存中進行緩存。
@Component
public class ConfigInitializer implements CommandLineRunner {
@Override
public void run(String... args) {
// 加載配置文件或數據庫配置信息
System.out.println("加載配置信息...");
// 例如加載外部配置文件
// Config config = configService.loadConfig();
}
}2.3 啟動時加載數據到緩存
有時你可能希望在應用啟動時將一些常用數據(如字典數據、熱點數據)加載到內存中,以提高訪問效率。
@Component
public class DataCacheInitializer implements ApplicationRunner {
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) {
System.out.println("啟動時加載字典數據到緩存...");
// 假設從數據庫加載數據到緩存
// List<Dict> dicts = dictService.loadAll();
// cacheService.cacheDicts(dicts);
}
}2.4 啟動時驗證環境配置
之前我們總結過:license版權證書生成與驗證,對license不太熟悉的可自行跳轉查看,簡單概括來說就是,你是軟件服務商,人家買了你的軟件,要求你部署到他們的服務器上,即本地化部署,這時候你就需要打成JAR包去客戶服務器上部署,如果就是簡單的java -jar jar包服務就能啟動跑起來了,那客戶就可以拿著你的jar包去賣了.....license就是為了堵住這個缺口,加了證書驗證,讓你換個環境跑不起來......
@Component
public class LicenseCheckApplicationRunner implements ApplicationRunner {
@Resource
private LicenseVerify licenseVerify;
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
LicenseContent content = licenseVerify.install();
}
}@Component
public class LicenseVerify {
@Resource
private LicenseProperties licenseProperties;
private static Logger logger = LogManager.getLogger(LicenseVerify.class);
private static final DateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
/**
* 安裝License證書
* 項目服務啟動時候安裝證書,檢驗合法性
* 此時根據開關驗證服務器系統信息
*/
public synchronized LicenseContent install() {
LicenseContent result = null;
try{
LicenseManager licenseManager = new LicenseManager(initLicenseParam());
licenseManager.uninstall();
result = licenseManager.install(new File(licenseProperties.getLicensePath()));
verifySystemInfo(result);
logger.info("證書安裝成功,證書有效期:{} - {}", df.format(result.getNotBefore()),
df.format(result.getNotAfter()));
}catch (Exception e){
logger.error("證書安裝失敗:", e);
throw new BizException("證書安裝失敗");
}
return result;
}
/**
* 校驗License證書, 在接口使用{@link com.plasticene.boot.license.core.anno.License}
* 時候進入license切面時候調用,此時無需再驗證服務器系統信息,驗證證書和有效期即可
*/
public boolean verify() {
try {
LicenseManager licenseManager = new LicenseManager(initLicenseParam());
LicenseContent licenseContent = licenseManager.verify();
verifyExpiry(licenseContent);
return true;
}catch (Exception e){
logger.error("證書校驗失敗:", e);
throw new BizException("證書檢驗失敗");
}
}
/**
* 初始化證書生成參數
*/
private LicenseParam initLicenseParam(){
Preferences preferences = Preferences.userNodeForPackage(LicenseVerify.class);
CipherParam cipherParam = new DefaultCipherParam(licenseProperties.getStorePass());
KeyStoreParam publicStoreParam = new CustomKeyStoreParam(LicenseVerify.class
,licenseProperties.getPublicKeysStorePath()
,licenseProperties.getPublicAlias()
,licenseProperties.getStorePass()
,null);
return new DefaultLicenseParam(licenseProperties.getSubject()
,preferences
,publicStoreParam
,cipherParam);
}
// 驗證證書有效期
private void verifyExpiry(LicenseContent licenseContent) {
Date expiry = licenseContent.getNotAfter();
Date current = new Date();
if (current.after(expiry)) {
throw new BizException("證書已過期");
}
}
private void verifySystemInfo(LicenseContent licenseContent) {
if (licenseProperties.getVerifySystemSwitch()) {
SystemInfo systemInfo = (SystemInfo) licenseContent.getExtra();
VerifySystemType verifySystemType = licenseProperties.getVerifySystemType();
switch (verifySystemType) {
case CPU_ID:
checkCpuId(systemInfo.getCpuId());
break;
case SYSTEM_UUID:
checkSystemUuid(systemInfo.getUuid());
break;
default:
}
}
}
private void checkCpuId(String cpuId) {
cpuId = cpuId.trim().toUpperCase();
String systemCpuId = DmcUtils.getCpuId().trim().toUpperCase();
logger.info("配置cpuId = {}, 系統cpuId = {}", cpuId, systemCpuId);
if (!Objects.equals(cpuId, systemCpuId)) {
throw new BizException("license檢驗cpuId不一致");
}
}
private void checkSystemUuid(String uuid) {
uuid = uuid.trim().toUpperCase();
String systemUuid = DmcUtils.getSystemUuid().trim().toUpperCase();
logger.info("配置uuid = {}, 系統uuid= {}", uuid, systemUuid);
if (!Objects.equals(uuid, systemUuid)) {
throw new BizException("license檢驗uuid不一致");
}
}
}如果證書校驗不通過,就會拋出異常,項目服務啟動失敗。
2.5 配合 @Order 使用
在同一個 Spring Boot 應用中,可能會有多個 CommandLineRunner 或 ApplicationRunner 實現類。如果你希望控制它們的執行順序,可以使用 @Order 注解,指定多個 Runner 的執行順序。
@Component
@Order(1) // 這個Runner會優先執行
public class FirstRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("FirstRunner running!");
}
}
@Component
@Order(2) // 這個Runner會后執行
public class SecondRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("SecondRunner running!");
}
}當應用啟動時,FirstRunner 會先執行,然后 SecondRunner 執行。
上面的示例都是使用CommandLineRunner,當然換成ApplicationRunner也是可以的。
項目推薦:基于SpringBoot2.x、SpringCloud和SpringCloudAlibaba企業級系統架構底層框架封裝,解決業務開發時常見的非功能性需求,防止重復造輪子,方便業務快速開發和企業技術棧框架統一管理。引入組件化的思想實現高內聚低耦合并且高度可配置化,做到可插拔。嚴格控制包依賴和統一版本管理,做到最少化依賴。注重代碼規范和注釋,非常適合個人學習和企業使用
Github地址:https://github.com/plasticene/plasticene-boot-starter-parent
Gitee地址:https://gitee.com/plasticene3/plasticene-boot-starter-parent
微信公眾號:Shepherd進階筆記
交流探討qun:Shepherd_126
3. CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner區別
直接看定義:
/**
* Interface used to indicate that a bean should <em>run</em> when it is contained within
* a {@link SpringApplication}. Multiple {@link CommandLineRunner} beans can be defined
* within the same application context and can be ordered using the {@link Ordered}
* interface or {@link Order @Order} annotation.
* <p>
* If you need access to {@link ApplicationArguments} instead of the raw String array
* consider using {@link ApplicationRunner}.
* 如果你需要訪問ApplicationArguments去替換掉字符串數組,可以考慮使用ApplicationRunner類。
* @author Dave Syer
* @since 1.0.0
* @see ApplicationRunner
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface CommandLineRunner {
/**
* Callback used to run the bean.
* @param args incoming main method arguments
* @throws Exception on error
*/
void run(String... args) throws Exception;
}ApplicationRunner 和 CommandLineRunner 類似,也是一個在應用啟動后執行的接口。但它更加強大,因為它使用了 ApplicationArguments 對象,而不僅僅是簡單的字符串數組。ApplicationArguments 允許更方便地處理傳入的參數,例如獲取無選項參數和帶選項參數
@Component
public class MyCommandLineRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("CommandLineRunner running!");
for (String arg : args) {
System.out.println("CommandLineRunner Arg: " + arg);
}
}
}
@Component
public class MyApplicationRunner implements ApplicationRunner {
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("ApplicationRunner running!");
for (String sourceArg : args.getSourceArgs()) {
System.out.println("ApplicationRunner Arg: " + sourceArg);
}
for (String nonOptionArg : args.getNonOptionArgs()) {
System.out.println("ApplicationRunner nonOptionArg: " + nonOptionArg);
}
for (String optionName : args.getOptionNames()) {
System.out.println("ApplicationRunner optionArg: " + args.getOptionValues(optionName));
}
}
}在IDEA中配置項目啟動參數:
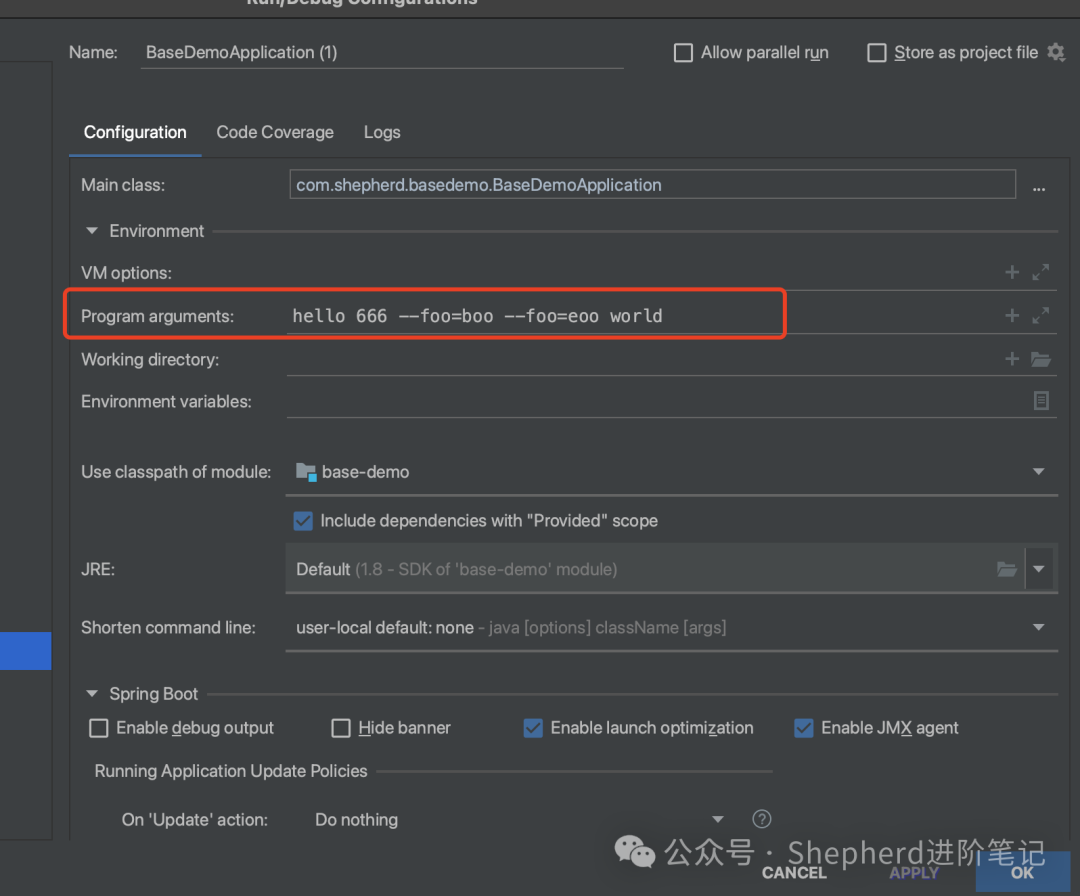 圖片
圖片
啟動服務,控制臺輸出如下:
ApplicationRunner running!
ApplicationRunner Arg: hello
ApplicationRunner Arg: 666
ApplicationRunner Arg: --foo=boo
ApplicationRunner Arg: --foo=eoo
ApplicationRunner Arg: world
ApplicationRunner nonOptionArg: hello
ApplicationRunner nonOptionArg: 666
ApplicationRunner nonOptionArg: world
ApplicationRunner optionArg: [boo, eoo]
CommandLineRunner running!
CommandLineRunner Arg: hello
CommandLineRunner Arg: 666
CommandLineRunner Arg: --foo=boo
CommandLineRunner Arg: --foo=eoo
CommandLineRunner Arg: world區別如下:
- 參數處理:
CommandLineRunner 接收一個 String... args,只是簡單地傳遞命令行參數。
ApplicationRunner 使用 ApplicationArguments 對象,它提供了對選項和非選項參數的更強大支持。
- 用法場景:
如果只是簡單地處理命令行參數或執行一些任務,CommandLineRunner 足夠。
如果你需要更靈活的方式來處理命令行選項和參數,ApplicationRunner 更合適。
參數管理:
CommandLineRunner 只能獲得原始的命令行參數。
ApplicationRunner 可以通過 ApplicationArguments 方便地獲取命令行選項、非選項參數,并區分它們。
4.實現原理
既然ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner是Spring Boot提供的兩個擴展點,我們就來看看項目啟動時它們是怎么執行的。
SpringApplication的核心入口方法#run():
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
Duration timeTakenToStartup = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), timeTakenToStartup);
}
listeners.started(context, timeTakenToStartup);
// 執行`ApplicationRunner`和`CommandLineRunner`的方法入庫
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
Duration timeTakenToReady = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
listeners.ready(context, timeTakenToReady);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}#callRunners(context, applicationArguments),從方法名就知道實現ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner的核心所在咯。
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<>();
// 從spring容器中獲取ApplicationRunner類型的bean放入到集合runners中
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());
// 從spring容器中獲取CommandLineRunner類型的bean放入到集合runners中
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());
// 排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);
for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<>(runners)) {
if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) {
callRunner((ApplicationRunner) runner, args);
}
if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) {
callRunner((CommandLineRunner) runner, args);
}
}
}最后通過#callRunner()執行run方法
private void callRunner(ApplicationRunner runner, ApplicationArguments args) {
try {
(runner).run(args);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to execute ApplicationRunner", ex);
}
}5.總結
CommandLineRunner 和 ApplicationRunner 常用于應用啟動后的初始化任務或一次性任務執行。它們允許你在 Spring 應用啟動完成后立即執行一些邏輯。ApplicationRunner 更適合需要處理命令行參數的場景,而 CommandLineRunner 更簡單直接。通過 @Order 注解可以控制多個 Runner 的執行順序,確保初始化操作按特定順序進行。
本文轉載自微信公眾號「Shepherd進階筆記」,可以通過以下二維碼關注。轉載本文請聯系公眾號。