8個計算機視覺深度學習中常見的Bug
給大家總結了8個計算機視覺深度學習中的常見bug,相信大家或多或少都遇到過,希望能幫助大家避免一些問題。
人是不完美的,我們經常在軟件中犯錯誤。有時這些錯誤很容易發現:你的代碼根本不能工作,你的應用程序崩潰等等。但是有些bug是隱藏的,這使得它們更加危險。
在解決深度學習問題時,由于一些不確定性,很容易出現這種類型的bug:很容易看到web應用程序路由請求是否正確,而不容易檢查你的梯度下降步驟是否正確。然而,有很多錯誤是可以避免的。
我想分享一些我的經驗,關于我在過去兩年的計算機視覺工作中看到或制造的錯誤。我(在會議上)談到過這個話題(https://datafest.ru/ia/),很多人在會后告訴我:“是的,我也有很多這樣的bug。”我希望我的文章可以幫助你至少避免其中的一些問題。
1. 翻轉圖片以及關鍵點.
假設在關鍵點檢測的問題上。數據看起來像一對圖像和一系列的關鍵點元組。其中每個關鍵點是一對x和y坐標。
讓我們對這個數據進行基礎的增強:
- def flip_img_and_keypoints(img: np.ndarray, kpts: Sequence[Sequence[int]]):
- img = np.fliplr(img)
- h, w, *_ = img.shape
- kpts = [(y, w - x) for y, x in kpts]
- return img, kpts
看起來是正確的,嗯?我們把它可視化。
- image = np.ones((10, 10), dtype=np.float32)
- kpts = [(0, 1), (2, 2)]
- image_flipped, kpts_flipped = flip_img_and_keypoints(image, kpts)
- img1 = image.copy()
- for y, x in kpts:
- img1[y, x] = 0
- img2 = image_flipped.copy()
- for y, x in kpts_flipped:
- img2[y, x] = 0
- _ = plt.imshow(np.hstack((img1, img2)))
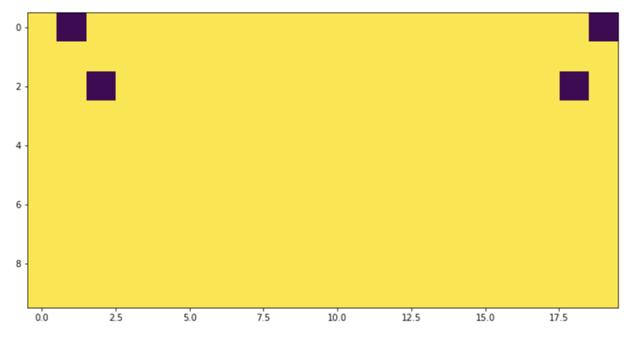
不對稱,看起來很奇怪!如果我們檢查極值呢?
- image = np.ones((10, 10), dtype=np.float32)
不好!這是一個典型的off-by-one錯誤。正確的代碼是這樣的:
- def flip_img_and_keypoints(img: np.ndarray, kpts: Sequence[Sequence[int]]):
- img = np.fliplr(img)
- h, w, *_ = img.shape
- kpts = [(y, w - x - 1) for y, x in kpts]
- return img, kpts
我們通過可視化發現了這個問題,但是,使用“x = 0”點進行單元測試也會有所幫助。一個有趣的事實是:有一個團隊中有三個人(包括我自己)獨立地犯了幾乎相同的錯誤。
2. 繼續是關鍵點相關的問題
即使在上面的函數被修復之后,仍然存在危險。現在更多的是語義,而不僅僅是一段代碼。
假設需要用兩只手掌來增強圖像。看起來很安全:手是左,右翻轉。
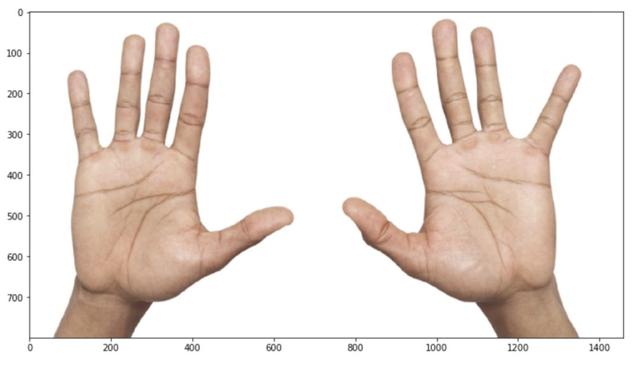
但是等等!我們對關鍵點的語義并不很了解。如果這個關鍵點的意思是這樣的:
- kpts = [
- (20, 20), # left pinky
- (20, 200), # right pinky
- ...
- ]
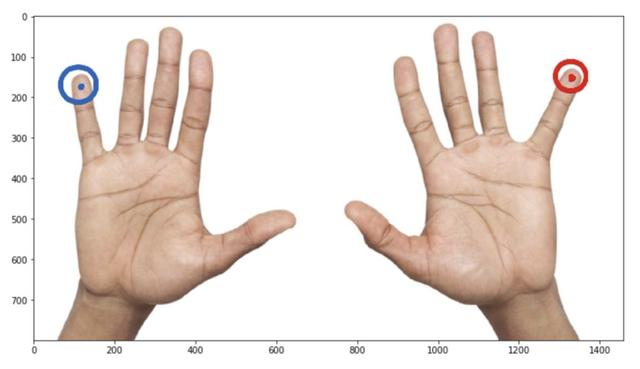
這意味著增強實際上改變了語義:左變成右,右變成左,但我們不交換數組中的關鍵點索引。它會給訓練帶來大量的噪音和更糟糕的度量。
我們應該吸取一個教訓:
- 在應用增強或其他花哨的功能之前,了解并考慮數據結構和語義
- 保持你的實驗原子性:添加一個小的變化(例如一個新的變換),檢查它如何進行,如果分數提高才加進去。
3. 編寫自己的損失函數
熟悉語義分割問題的人可能知道IoU指標。不幸的是,我們不能直接用SGD來優化它,所以常用的方法是用可微損失函數來近似它。
- def iou_continuous_loss(y_pred, y_true):
- eps = 1e-6
- def _sum(x):
- return x.sum(-1).sum(-1)
- numerator = (_sum(y_true * y_pred) + eps)
- denominator = (_sum(y_true ** 2) + _sum(y_pred ** 2)
- - _sum(y_true * y_pred) + eps)
- return (numerator / denominator).mean()
看起來不錯,我們先做個小的檢查:
- In [3]: ones = np.ones((1, 3, 10, 10))
- ...: x1 = iou_continuous_loss(ones * 0.01, ones)
- ...: x2 = iou_continuous_loss(ones * 0.99, ones)
- In [4]: x1, x2
- Out[4]: (0.010099999897990103, 0.9998990001020204)
在 x1中,我們計算了一些與ground truth完全不同的東西的損失,而 x2則是非常接近ground truth的東西的結果。我們預計 x1會很大,因為預測是錯誤的, x2應該接近于零。怎么了?
上面的函數是對metric的一個很好的近似。metric不是一種損失:它通常(包括這種情況)越高越好。當我們使用SGD來最小化損失時,我們應該使用一些相反的東西:
- def iou_continuous(y_pred, y_true):
- eps = 1e-6
- def _sum(x):
- return x.sum(-1).sum(-1)
- numerator = (_sum(y_true * y_pred) + eps)
- denominator = (_sum(y_true ** 2) + _sum(y_pred ** 2)
- - _sum(y_true * y_pred) + eps)
- return (numerator / denominator).mean()
- def iou_continuous_loss(y_pred, y_true):
- return 1 - iou_continuous(y_pred, y_true)
這些問題可以從兩個方面來確定:
- 編寫一個單元測試,檢查損失的方向:形式化的期望,更接近ground truth應該輸出更低的損失。
- 運行一個健全的檢查,讓你的模型在單個batch中過擬合。
4. 當我們使用Pytorch的時候
假設有一個預先訓練好的模型,開始做infer。
- from ceevee.base import AbstractPredictor
- class MySuperPredictor(AbstractPredictor):
- def __init__(self,
- weights_path: str,
- ):
- super().__init__()
- self.model = self._load_model(weights_path=weights_path)
- def process(self, x, *kw):
- with torch.no_grad():
- res = self.model(x)
- return res
- @staticmethod
- def _load_model(weights_path):
- model = ModelClass()
- weights = torch.load(weights_path, map_location='cpu')
- model.load_state_dict(weights)
- return model
這個代碼正確嗎?也許!這確實適用于某些模型。例如,當模型沒有dropout或norm層,如 torch.nn.BatchNorm2d。或者當模型需要為每個圖像使用實際的norm統計量時(例如,許多基于pix2pix的架構需要它)。
但是對于大多數計算機視覺應用程序來說,代碼忽略了一些重要的東西:切換到評估模式。
如果試圖將動態PyTorch圖轉換為靜態PyTorch圖,這個問題很容易識別。 torch.jit用于這種轉換。
- In [3]: model = nn.Sequential(
- ...: nn.Linear(10, 10),
- ...: nn.Dropout(.5)
- ...: )
- ...:
- ...: traced_model = torch.jit.trace(model, torch.rand(10))
- /Users/Arseny/.pyenv/versions/3.6.6/lib/python3.6/site-packages/torch/jit/__init__.py:914: TracerWarning: Trace had nondeterministic nodes. Did you forget call .eval() on your model? Nodes:
- %12 : Float(10) = aten::dropout(%input, %10, %11), scope: Sequential/Dropout[1] # /Users/Arseny/.pyenv/versions/3.6.6/lib/python3.6/site-packages/torch/nn/functional.py:806:0
- This may cause errors in trace checking. To disable trace checking, pass check_trace=False to torch.jit.trace()
- check_tolerance, _force_outplace, True, _module_class)
- /Users/Arseny/.pyenv/versions/3.6.6/lib/python3.6/site-packages/torch/jit/__init__.py:914: TracerWarning: Output nr 1. of the traced function does not match the corresponding output of the Python function. Detailed error:
- Not within tolerance rtol=1e-05 atol=1e-05 at input[5] (0.0 vs. 0.5454154014587402) and 5 other locations (60.00%)
- check_tolerance, _force_outplace, True, _module_class)
簡單的修復一下:
- In [4]: model = nn.Sequential(
- ...: nn.Linear(10, 10),
- ...: nn.Dropout(.5)
- ...: )
- ...:
- ...: traced_model = torch.jit.trace(model.eval(), torch.rand(10))
- # No more warnings!
在這種情況下, torch.jit.trace將模型運行幾次并比較結果。這里的差別是可疑的。
然而 torch.jit.trace在這里不是萬能藥。這是一種應該知道和記住的細微差別。
5. 復制粘貼的問題
很多東西都是成對存在的:訓練和驗證、寬度和高度、緯度和經度……
- def make_dataloaders(train_cfg, val_cfg, batch_size):
- train = Dataset.from_config(train_cfg)
- val = Dataset.from_config(val_cfg)
- shared_params = {'batch_size': batch_size, 'shuffle': True, 'num_workers': cpu_count()}
- train = DataLoader(train, **shared_params)
- val = DataLoader(train, **shared_params)
- return train, val
不僅僅是我犯了愚蠢的錯誤。例如,在非常流行的albumentations庫也有一個類似的版本。
- # https://github.com/albu/albumentations/blob/0.3.0/albumentations/augmentations/transforms.py
- def apply_to_keypoint(self, keypoint, crop_height=0, crop_width=0, h_start=0, w_start=0, rows=0, cols=0, **params):
- keypoint = F.keypoint_random_crop(keypoint, crop_height, crop_width, h_start, w_start, rows, cols)
- scale_x = self.width / crop_height
- scale_y = self.height / crop_height
- keypoint = F.keypoint_scale(keypoint, scale_x, scale_y)
- return keypoint
別擔心,已經修改好了。
如何避免?不要復制和粘貼代碼,盡量以不需要復制和粘貼的方式編寫代碼。
- datasets = []
- data_a = get_dataset(MyDataset(config['dataset_a']), config['shared_param'], param_a)
- datasets.append(data_a)
- data_b = get_dataset(MyDataset(config['dataset_b']), config['shared_param'], param_b)
- datasets.append(data_b)
- datasets = []
- for name, param in zip(('dataset_a', 'dataset_b'),
- (param_a, param_b),
- ):
- datasets.append(get_dataset(MyDataset(config[name]), config['shared_param'], param))
6. 合適的數據類型
讓我們編寫一個新的增強:
- def add_noise(img: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
- mask = np.random.rand(*img.shape) + .5
- img = img.astype('float32') * mask
- return img.astype('uint8')

圖像已被更改。這是我們所期望的嗎?嗯,也許它改變得太多了。
這里有一個危險的操作:將 float32 轉換為 uint8。它可能會導致溢出:
- def add_noise(img: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
- mask = np.random.rand(*img.shape) + .5
- img = img.astype('float32') * mask
- return np.clip(img, 0, 255).astype('uint8')
- img = add_noise(cv2.imread('two_hands.jpg')[:, :, ::-1])
- _ = plt.imshow(img)
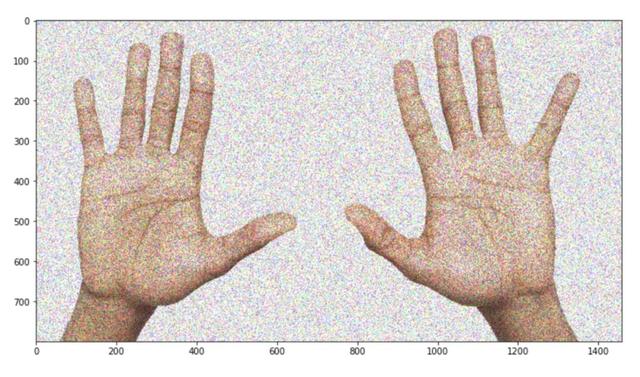
看起來好多了,是吧?
順便說一句,還有一種方法可以避免這個問題:不要重新發明輪子,不要從頭開始編寫增強代碼并使用現有的擴展: albumentations.augmentations.transforms.GaussNoise。
我曾經做過另一個同樣起源的bug。
- raw_mask = cv2.imread('mask_small.png')
- mask = raw_mask.astype('float32') / 255
- mask = cv2.resize(mask, (64, 64), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
- mask = cv2.resize(mask, (128, 128), interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
- mask = (mask * 255).astype('uint8')
- _ = plt.imshow(np.hstack((raw_mask, mask)))
這里出了什么問題?首先,用三次插值調整掩模的大小是一個壞主意。同樣的問題 float32到 uint8:三次插值可以輸出值大于輸入,這會導致溢出。

我在做可視化的時候發現了這個問題。在你的訓練循環中到處放置斷言也是一個好主意。
7. 拼寫錯誤
假設需要對全卷積網絡(如語義分割問題)和一個巨大的圖像進行推理。該圖像是如此巨大,沒有機會把它放在你的GPU中,它可以是一個醫療或衛星圖像。
在這種情況下,可以將圖像分割成網格,獨立地對每一塊進行推理,最后合并。此外,一些預測交叉可能有助于平滑邊界附近的artifacts。
- from tqdm import tqdm
- class GridPredictor:
- """
- This class can be used to predict a segmentation mask for the big image
- when you have GPU memory limitation
- """
- def __init__(self, predictor: AbstractPredictor, size: int, stride: Optional[int] = None):
- self.predictor = predictor
- self.size = size
- self.stride = stride if stride is not None else size // 2
- def __call__(self, x: np.ndarray):
- h, w, _ = x.shape
- mask = np.zeros((h, w, 1), dtype='float32')
- weights = mask.copy()
- for i in tqdm(range(0, h - 1, self.stride)):
- for j in range(0, w - 1, self.stride):
- a, b, c, d = i, min(h, i + self.size), j, min(w, j + self.size)
- patch = x[a:b, c:d, :]
- mask[a:b, c:d, :] += np.expand_dims(self.predictor(patch), -1)
- weights[a:b, c:d, :] = 1
- return mask / weights
有一個符號輸入錯誤,代碼段足夠大,可以很容易地找到它。我懷疑僅僅通過代碼就能快速識別它。但是很容易檢查代碼是否正確:
- class Model(nn.Module):
- def forward(self, x):
- return x.mean(axis=-1)
- model = Model()
- grid_predictor = GridPredictor(model, size=128, stride=64)
- simple_pred = np.expand_dims(model(img), -1)
- grid_pred = grid_predictor(img)
- np.testing.assert_allclose(simple_pred, grid_pred, atol=.001)
- ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
- AssertionError Traceback (most recent call last)
- <ipython-input-24-a72034c717e9> in <module>
- 9 grid_pred = grid_predictor(img)
- 10
- ---> 11 np.testing.assert_allclose(simple_pred, grid_pred, atol=.001)
- ~/.pyenv/versions/3.6.6/lib/python3.6/site-packages/numpy/testing/_private/utils.py in assert_allclose(actual, desired, rtol, atol, equal_nan, err_msg, verbose)
- 1513 header = 'Not equal to tolerance rtol=%g, atol=%g' % (rtol, atol)
- 1514 assert_array_compare(compare, actual, desired, err_msg=str(err_msg),
- -> 1515 verbose=verbose, header=header, equal_nan=equal_nan)
- 1516
- 1517
- ~/.pyenv/versions/3.6.6/lib/python3.6/site-packages/numpy/testing/_private/utils.py in assert_array_compare(comparison, x, y, err_msg, verbose, header, precision, equal_nan, equal_inf)
- 839 verbose=verbose, header=header,
- 840 names=('x', 'y'), precision=precision)
- --> 841 raise AssertionError(msg)
- 842 except ValueError:
- 843 import traceback
- AssertionError:
- Not equal to tolerance rtol=1e-07, atol=0.001
- Mismatch: 99.6%
- Max absolute difference: 765.
- Max relative difference: 0.75000001
- x: array([[[215.333333],
- [192.666667],
- [250. ],...
- y: array([[[ 215.33333],
- [ 192.66667],
- [ 250. ],...
下面是 __call__方法的正確版本:
- def __call__(self, x: np.ndarray):
- h, w, _ = x.shape
- mask = np.zeros((h, w, 1), dtype='float32')
- weights = mask.copy()
- for i in tqdm(range(0, h - 1, self.stride)):
- for j in range(0, w - 1, self.stride):
- a, b, c, d = i, min(h, i + self.size), j, min(w, j + self.size)
- patch = x[a:b, c:d, :]
- mask[a:b, c:d, :] += np.expand_dims(self.predictor(patch), -1)
- weights[a:b, c:d, :] += 1
- return mask / weights
如果你仍然不知道問題出在哪里,請注意 weights[a:b,c:d,:]+=1這一行。
8. Imagenet歸一化
當一個人需要進行轉移學習時,用訓練Imagenet時的方法將圖像歸一化通常是一個好主意。
讓我們使用我們已經熟悉的albumentations庫。
- from albumentations import Normalize
- norm = Normalize()
- img = cv2.imread('img_small.jpg')
- mask = cv2.imread('mask_small.png', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
- mask = np.expand_dims(mask, -1) # shape (64, 64) -> shape (64, 64, 1)
- normed = norm(image=img, mask=mask)
- img, mask = [normed[x] for x in ['image', 'mask']]
- def img_to_batch(x):
- x = np.transpose(x, (2, 0, 1)).astype('float32')
- return torch.from_numpy(np.expand_dims(x, 0))
- img, mask = map(img_to_batch, (img, mask))
- criterion = F.binary_cross_entropy
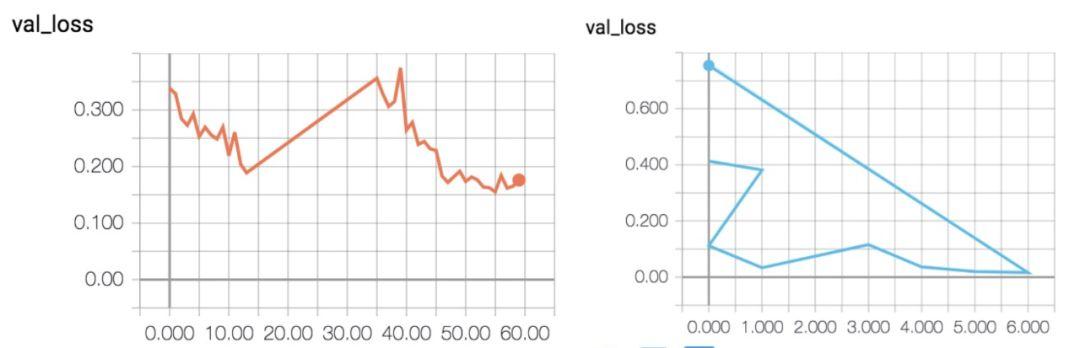
現在是時候訓練一個網絡并對單個圖像進行過度擬合了——正如我所提到的,這是一種很好的調試技術:
- model_a = UNet(3, 1)
- optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model_a.parameters(), lr=1e-3)
- losses = []
- for t in tqdm(range(20)):
- loss = criterion(model_a(img), mask)
- losses.append(loss.item())
- optimizer.zero_grad()
- loss.backward()
- optimizer.step()
- _ = plt.plot(losses)
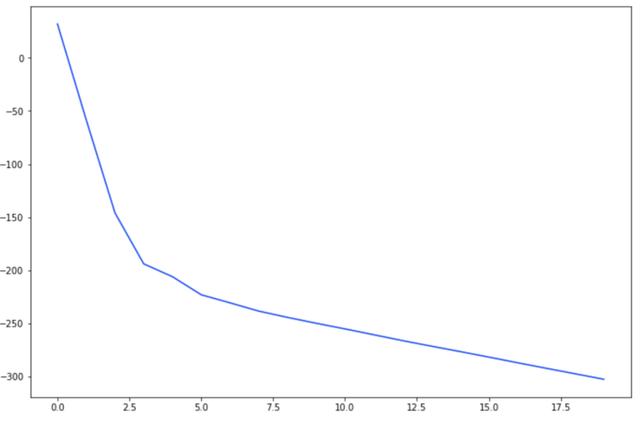
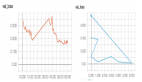
曲率看起來很好,但是交叉熵的損失值-300是不可預料的。是什么問題?
歸一化處理圖像效果很好,但是mask沒有:需要手動縮放到 [0,1]。
- model_b = UNet(3, 1)
- optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model_b.parameters(), lr=1e-3)
- losses = []
- for t in tqdm(range(20)):
- loss = criterion(model_b(img), mask / 255.)
- losses.append(loss.item())
- optimizer.zero_grad()
- loss.backward()
- optimizer.step()
- _ = plt.plot(losses)
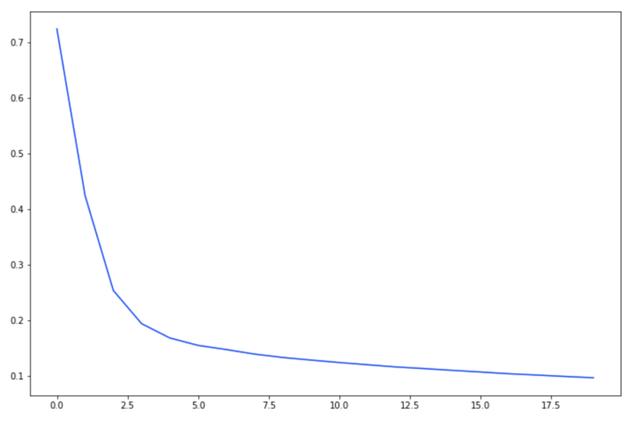
訓練循環的簡單運行時斷言(例如 assertmask.max()<=1會很快檢測到問題。同樣,也可以是單元測試。
總結
- 測試很有必要
- 運行時斷言可以用于訓練的pipeline;
- 可視化是一種幸福
- 復制粘貼是一種詛咒
- 沒有什么是靈丹妙藥,一個機器學習工程師必須總是小心(或只是受苦)。