譯者 | 朱先忠
審校 | 重樓
LangChain框架是一個非常強大的工具,它大大加快了LLM在項目和代理開發中的有效使用。該框架提供了一種高級抽象,允許開發人員立即開始使用模型并將其集成到他們的產品中。但是另一方面,了解LangChain的核心概念(例如Runnable的架構)對于構建LLM代理和鏈的開發人員非常有益,因為它提供了一種結構化的方法和對使用框架的洞察力。

LangChain架構基礎
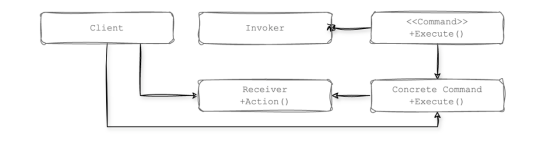
LangChain中的Runnable架構基于命令模式的原理構建,命令模式是一種將請求封裝為對象的行為設計模式。這種設計有助于參數化、排隊和動態執行命令,使Runnable對象在各種工作流中模塊化、可組合和可管理。
Runnable對象特別適合工作流管理、順序任務執行、處理條件邏輯以及與外部系統交互,它們提供靈活性、可重用性和模塊化。你可以動態地將任務鏈接在一起以創建復雜的行為場景,同時保持干凈且易于管理的代碼結構。
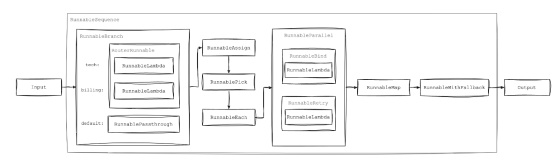 Runnable鏈的可能配置之一
Runnable鏈的可能配置之一
LangChain中執行特定任務的大多數高級對象都實現了Runnable類。你計劃包含在鏈中的任何對象也必須以某種方式實現Runnable類。有趣的是,Runnable充當命令的抽象或一個具體命令,同時也充當了一個調用者和接收者角色。
一個值得注意的例子是此類中提供的管道方法,它專門用于創建鏈。此方法允許無縫組合多個Runnable,使其成為在LangChain中構建和執行工作流的基石。
在上圖中,你可以看到Runnable如何與其各種實現一起運行。接下來,我們將在本文中詳細研究這些實現。
創建Runnable
實際上,有兩種方法可以創建Runnable:通過RunnableLambda或擴展基Runnable類。
將RunnableLambda用于簡單函數
創建Runnable的最簡單方法是使用RunnableLambda。此類允許你將任何函數包裝為Runnable,從而允許動態行為而無需自定義類。
import { RunnableLambda } from "@langchain/core/runnables";
//定義一個簡單函數
const toUpperCase = (text: string): string => text.toUpperCase();
//將函數包裝為Runnable
const upperCaseRunnable = RunnableLambda.from(toUpperCase);
//調用Runnable
const result = await upperCaseRunnable.invoke("hello world");
//輸出: "HELLO WORLD"擴展Runnable基類
對于更高級的使用場景,你可以擴展Runnable基類。此方法可完全控制執行生命周期,包括調用、批處理和流等方法。
import { Runnable } from "@langchain/core/runnables";
class GreetUserRunnable extends Runnable<string, string> {
lc_namespace = ["GreetUser"];
onStart(data: { input: string }) {
console.log(`Starting with input: ${data.input}`);
}
onEnd(data: { result: string }) {
console.log(`Finished with result: ${data.result}`);
}
onError(error: unknown) {
console.error(`Error occurred: ${(error as Error).message}`);
}
//自定義執行邏輯
async invoke(name: string): Promise<string> {
this.onStart({ input: name });
try {
const greeting = `Hello, ${name}!`;
this.onEnd({ result: greeting });
return greeting;
} catch (error) {
this.onError(error);
throw error;
}
}
}使用Runnable構建工作流
LangChain中的Runnable架構通過按功能分組的專用Runnable進行了擴展,使其用途廣泛且適用于各種應用程序。
路由和分支類型
根據條件或輸入管理執行流程的Runnable有:
RouterRunnable
根據給定的鍵值將輸入定向到特定的Runnable,類似于switch-case語句。適用于基于運行時參數的動態任務執行。
import { RouterRunnable, RunnableLambda } from "@langchain/core/runnables";
const router = new RouterRunnable({
runnables: {
billing: RunnableLambda.from((query: string) => `Billing Department: ${query}`),
technical: RunnableLambda.from((query: string) => `Technical Support: ${query}`),
general: RunnableLambda.from((query: string) => `General Inquiry: ${query}`),
},
});
//路由一個賬單問題
const result1 = await router.invoke({ key: "billing", input: "I have a question about my invoice." });
// 輸出: "Billing Department: I have a question about my invoice."
//路由一個技術問題
const result2 = await router.invoke({ key: "technical", input: "My internet is not working." });
// 輸出: "Technical Support: My internet is not working."RunnableBranch
根據條件檢查從多個選項中執行特定的Runnable,使工作流能夠適應不同的輸入場景。
const branch = RunnableBranch.from([
[
(user: { age: number }) => user.age < 18,
RunnableLambda.from((user) => `Hey ${user.name}, check out our new teen collection!`),
],
[
(user: { age: number }) => user.age >= 18 && user.age < 30,
RunnableLambda.from((user) => `Hi ${user.name}, explore our trendy outfits for young adults!`),
],
RunnableLambda.from((user) => `Hello ${user.name}, discover our premium range!`),
]);
const result = await branch.invoke({ name: "Alice", age: 25 });
// 輸出: "Hi Alice, explore our trendy outfits for young adults!"數據操作和分配類型
轉換或準備數據以用于后續任務的Runnable有:
RunnableAssign
通過添加新字段或更新現有字段來增強或修改輸入數據,為后續處理步驟做好準備。
import { RunnableAssign, RunnableLambda } from "@langchain/core/runnables";
const getGeolocation = RunnableLambda.from(async (x: { ip: string }) => {
//模擬一個API調用來獲取地理定位
return { location: `Location for IP ${x.ip}` };
});
const runnableAssign = new RunnableAssign({ getGeolocation });
const res = await runnableAssign.invoke({ name: "John Doe", ip: "192.168.1.1" });
// 輸出結果: { name: "John Doe", ip: "192.168.1.1", getGeolocation: { location: "Location for IP 192.168.1.1" } }RunnablePick
從輸入數據中選擇并提取特定字段,從而可以對相關信息進行重點處理。
import { RunnablePick } from "@langchain/core/runnables";
const orderData = {
orderId: "12345",
customerEmail: "customer@example.com",
items: [{ productId: "A1", quantity: 2 }],
totalAmount: 99.99,
shippingAddress: "123 Main St",
};
const receiptInfoRunnable = new RunnablePick(["orderId", "customerEmail", "totalAmount"]);
const res = await receiptInfoRunnable.invoke(orderData);
// 輸出結果: { orderId: '12345', customerEmail: 'customer@example.com', totalAmount: 99.99 }RunnablePassthrough
不做任何更改地傳遞輸入數據,這對于維護工作流中的數據完整性非常有用。
const chain = RunnableSequence.from([
{
question: new RunnablePassthrough(),
context: async () => loadContextFromStore(),
},
prompt,
llm,
outputParser,
]);
const response = await chain.invoke(
"I can pass a single string instead of an object since I'm using `RunnablePassthrough`."
);RunnableMap
將轉換應用于映射對象中的每個字段,從而實現對鍵值對的單獨處理。
const sensorDataRunnable = RunnableMap.from({
temperature: RunnableLambda.from((data: { temp: number }) => `Temperature is ${data.temp}°C`),
humidity: RunnableLambda.from((data: { humidity: number }) => `Humidity is ${data.humidity}%`),
});
const result = await sensorDataRunnable.invoke({ temp: 22, humidity: 45 });
// 輸出結果: { temperature: 'Temperature is 22°C', humidity: 'Humidity is 45%' }序列和工作流組合類型
可按順序構造和執行任務的Runnable,支持創建復雜的工作流:
RunnableSequence
以線性方式鏈接多個Runnable,其中一個Runnable的輸出成為下一個Runnable的輸入,形成逐步處理的管道結構。
const imageProcessingChain = RunnableSequence.from([
readImageRunnable,
resizeImageRunnable,
applyFilterRunnable,
saveImageRunnable,
]);
const result = await imageProcessingChain.invoke('path/to/input/image.jpg');RunnableEach
將Runnable應用于集合中的每個元素,類似于數組上的映射函數,允許批處理。
import { RunnableEach, RunnableLambda } from "@langchain/core/runnables";
const personalizeEmail = RunnableLambda.from((name: string) => `Dear ${name}, we have an offer for you!`);
const sendEmail = emailSendingRunnable; // 假設這是在其他地方定義的
const emailChain = new RunnableEach({
bound: personalizeEmail.pipe(sendEmail),
});
const result = await emailChain.invoke(["Alice", "Bob", "Carol"]);
//將電子郵件發送到:Alice, Bob, and Carol.RunnableParallel
在同一輸入上同時執行多個Runnable,從而實現并發處理以提高效率。
import { RunnableLambda, RunnableParallel } from "@langchain/core/runnables";
const calculateMean = RunnableLambda.from((data: number[]) => {
return data.reduce((a, b) => a + b, 0) / data.length;
});
const calculateMedian = RunnableLambda.from((data: number[]) => {
const sorted = data.slice().sort((a, b) => a - b);
const mid = Math.floor(sorted.length / 2);
return sorted.length % 2 !== 0 ? sorted[mid] : (sorted[mid - 1] + sorted[mid]) / 2;
});
const calculateMode = RunnableLambda.from((data: number[]) => {
const frequency: { [key: number]: number } = {};
let maxFreq = 0;
let modes: number[] = [];
data.forEach((item) => {
frequency[item] = (frequency[item] || 0) + 1;
if (frequency[item] > maxFreq) {
maxFreq = frequency[item];
modes = [item];
} else if (frequency[item] === maxFreq) {
modes.push(item);
}
});
return modes;
});
const analysisChain = RunnableParallel.from({
mean: calculateMean,
median: calculateMedian,
mode: calculateMode,
});
const res = await analysisChain.invoke([1, 2, 2, 3, 4]);
// 輸出結果: { mean: 2.4, median: 2, mode: [2] }錯誤處理、彈性和配置類型
通過重試機制和回退選項增強穩健性的Runnable有:
RunnableBinding
通過預設某些參數或配置創建自定義Runnable,允許針對特定上下文定制可重復使用的組件。
import { RunnableConfig, RunnableLambda } from "@langchain/core/runnables";
const queryDatabase = (query: string, config?: RunnableConfig) => {
const dbConfig = config?.configurable?.dbConfig;
//使用dbConfig建立連接并執行查詢
return `Executed query on ${dbConfig.host}: ${query}`;
};
const runnable = RunnableLambda.from(queryDatabase);
// 綁定用在不同環境中的配置
const prodRunnable = runnable.bind({ configurable: { dbConfig: { host: 'prod.db.example.com' } } });
const testRunnable = runnable.bind({ configurable: { dbConfig: { host: 'test.db.example.com' } } });
const result1 = await prodRunnable.invoke("SELECT * FROM users;");
// 輸出結果: "Executed query on prod.db.example.com: SELECT * FROM users;"
const result2 = await testRunnable.invoke("SELECT * FROM users;");
// 輸出結果: "Executed query on test.db.example.com: SELECT * FROM users;"RunnableRetry
根據指定的重試策略在失敗時自動重試Runnable,增強對瞬態錯誤的恢復能力。
import { RunnableLambda } from "@langchain/core/runnables";
const fetchWeatherData = async (location: string): Promise<string> => {
//模擬一個可能會失敗的API調用
if (Math.random() < 0.7) {
throw new Error("Network error");
}
return `Weather data for ${location}`;
};
const fetchWeatherLambda = RunnableLambda.from(fetchWeatherData);
//應用重試邏輯
const fetchWeatherWithRetry = fetchWeatherLambda.withRetry({ stopAfterAttempt: 5 });
try {
const res = await fetchWeatherWithRetry.invoke("New York");
console.log(res);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Failed to fetch weather data after retries:", error.message);
}RunnableWithFallbacks
如果主Runnable失敗,則提供要執行的替代Runnable,以確保工作流程可以繼續或正常降級。
import { RunnableLambda, RunnableWithFallbacks } from "@langchain/core/runnables";
const primaryDataSource = async (id: string): Promise<string> => {
//模擬失敗故障
throw new Error("Primary data source is unavailable");
};
const secondaryDataSource = async (id: string): Promise<string> => {
return `Data for ${id} from secondary source`;
};
const primaryRunnable = RunnableLambda.from(primaryDataSource);
const fallbackRunnable = RunnableLambda.from(secondaryDataSource);
//帶回退的設置
const dataRunnable = primaryRunnable.withFallbacks([fallbackRunnable]);
const res = await dataRunnable.invoke("item123");
// 輸出結果: "Data for item123 from secondary source"整合
在前面的部分中,我們探討了單個Runnable及其在構建模塊化工作流中的作用。現在,讓我們看看如何組合這些Runnable來創建全面的實際應用程序。以下三個示例演示了如何集成多個Runnable來解決復雜問題。
示例1:智能文檔處理管道
現在,我們假定有一家公司希望自動處理發票、收據和合同等傳入文檔。開發的軟件系統目標是對文檔類型進行分類、提取相關數據、驗證數據并將其存儲在數據庫中,并且能夠妥善處理錯誤,并在發生瞬時故障時重試操作。
使用的Runnable有RunnableSequence、RouterRunnable、RunnableParallel、RunnableRetry、RunnableWithFallbacks、RunnableAssign、RunnableLambda等,關鍵代碼如下:
import {
RunnableSequence,
RouterRunnable,
RunnableLambda,
} from "@langchain/core/runnables";
//定義一個統一的輸出類型
type UnifiedOutput = {
type: string;
amount?: number;
dueDate?: string;
client?: string;
parties?: string[];
term?: string;
total?: number;
items?: string[];
};
// 步驟1:OCR處理(用函數模擬)
const ocrRunnable = RunnableLambda.from(async (imageBuffer: string) => {
//模擬OCR處理
return "Extracted text: Invoice for Acme Corp";
});
//步驟2:文件分類
const classifyDocument = RunnableLambda.from(async (text: string) => {
//模擬文件分類
if (text.includes("Invoice")) return "invoice";
if (text.includes("Contract")) return "contract";
return "receipt";
});
//步驟3:每種文檔類型的數據提取Runnables
const extractInvoiceData = RunnableLambda.from(
async (text: string): Promise<UnifiedOutput> => {
// 提取特定于發票的數據
return {
type: "invoice",
amount: 1000,
dueDate: "2024-12-31",
client: "Acme Corp",
};
}
);
const extractContractData = RunnableLambda.from(
async (text: string): Promise<UnifiedOutput> => {
// 提取特定于合同的數據
return {
type: "contract",
parties: ["Company A", "Company B"],
term: "2 years",
};
}
);
const extractReceiptData = RunnableLambda.from(
async (text: string): Promise<UnifiedOutput> => {
//提取特定于收據的數據
return { type: "receipt", total: 50, items: ["Item1", "Item2"] };
}
);
const dataExtractionRouter = new RouterRunnable({
runnables: {
invoice: extractInvoiceData,
contract: extractContractData,
receipt: extractReceiptData,
},
});
// 步驟5:數據驗證
const validateData = RunnableLambda.from(async (data: UnifiedOutput) => {
//執行驗證邏輯
if (!data || !data.type)
throw new Error("Validation failed: Data is missing or invalid");
return { ...data, isValid: true };
});
// 步驟6:保存到數據庫(使用一個函數進行模擬)
const saveToDatabase = RunnableLambda.from(async (data: UnifiedOutput) => {
// 模擬保存到數據庫
return `Data saved: ${JSON.stringify(data)}`;
});
//步驟7:構建工作流序列
const documentProcessingWorkflow = RunnableSequence.from<string, any>([
ocrRunnable,
classifyDocument,
dataExtractionRouter,
validateData,
saveToDatabase.withRetry({ stopAfterAttempt: 3 }),
]);
// 步驟8:添加帶有回退支持的錯誤處理
const workflowWithFallback = documentProcessingWorkflow.withFallbacks({
fallbacks: [
RunnableLambda.from(async () => {
return "An error occurred. Please try again later.";
}),
],
});
//執行工作流
(async () => {
try {
const result = await workflowWithFallback.invoke("Document image bytes");
console.log(result);
//期望的輸出結果: "Data saved: { type: 'invoice', amount: 1000, dueDate: '2024-12-31', client: 'Acme Corp', isValid: true }"
} catch (error: any) {
console.error("Failed to process document:", (error as Error).message);
}
})();在上面代碼中,工作流首先使用ocrRunnable將文檔圖像轉換為文本。提取的文本被分類為文檔類型(發票、合同或收據)。RouterRunnable根據文檔類型將文本定向到適當的數據提取Runnable。提取的數據經過驗證,然后保存到數據庫。RunnableRetry確保在發生瞬時故障時重試保存最多三次。如果任一步驟失敗,RunnableWithFallbacks會提供回退消息以妥善處理錯誤。
示例2:個性化推薦引擎
電子商務平臺希望根據用戶的瀏覽歷史和偏好為他們提供個性化的產品推薦。
使用的Runnable有RunnableParallel、RunnableMap、RunnableBranch、RunnableWithFallbacks等,相關代碼如下:
import {
RunnableParallel,
RunnableMap,
RunnableBranch,
RunnableSequence,
RunnableLambda,
} from "@langchain/core/runnables";
// 步驟1:并行地從多個來源獲取用戶數據
const fetchUserData = RunnableParallel.from({
browsingHistory: RunnableLambda.from(async (userId) => {
// 模擬獲取瀏覽歷史記錄
return ["Item1", "Item2"];
}),
purchaseHistory: RunnableLambda.from(async (userId) => {
// 模擬獲取購買歷史記錄
return ["Item3"];
}),
});
// 步驟2:映射到獲取的數據上以進行處理
const processUserData = RunnableMap.from({
browsingHistory: RunnableLambda.from((history: any[]) => {
//處理瀏覽歷史記錄
return history.map((item) => `Processed ${item}`);
}),
purchaseHistory: RunnableLambda.from((history: any[]) => {
// 處理采購歷史記錄
return history.map((item) => `Processed ${item}`);
}),
});
//步驟3:定義推薦算法
const newUserRecommendations = RunnableLambda.from(async (user) => {
// 針對新用戶的邏輯
return ["Product A", "Product B", "Product C"];
});
const returningUserRecommendations = RunnableLambda.from(async (user) => {
//基于歷史記錄返回用戶的邏輯
return ["Product X", "Product Y", "Product Z"];
});
// 步驟4:基于用戶類型的分支處理
const recommendationBranch = RunnableBranch.from([
[(user: any) => user.isNew, newUserRecommendations],
returningUserRecommendations,
]);
//步驟5:創建一個回退推薦系統
const defaultRecommendations = RunnableLambda.from(async (user) => {
//默認的推薦
return ["Default Product 1", "Default Product 2"];
});
const recommendationWithFallback = recommendationBranch.withFallbacks([
defaultRecommendations,
]);
// 步驟6:對整個工作流進行排隊操作
const recommendationWorkflow = RunnableSequence.from([
fetchUserData,
processUserData,
(data) => ({ ...data, isNew: data.purchaseHistory.length === 0 }),
recommendationWithFallback,
]);
// 用法
const userId = "user123";
const recommendations = recommendationWorkflow.invoke(userId);
// 輸出:基于用戶數據的個性化推薦在上面代碼中,工作流首先使用RunnableParallel同時獲取用戶的瀏覽歷史、購買歷史和個人資料。然后,使用RunnableMap單獨處理每條數據,為生成推薦做好準備。
RunnableBranch根據用戶的個人資料決定使用哪種推薦算法:
- 如果用戶是高級會員(isPremiumMembe為true),則使用premiumUserRecommendations。
- 如果用戶沒有購買歷史(表示是新用戶),則使用newUserRecommendations。
- 否則,默認為regularUserRecommendations。
如果推薦過程中的任一步驟失敗,RunnableWithFallbacks可確保系統提供一組默認推薦,從而保持良好的用戶體驗。
最后,RunnableSequence協調整個工作流,確保每個步驟都按正確的順序進行。工作流通過使用userId調用來執行,并根據用戶的數據輸出個性化推薦。
示例3:用于分析的數據處理管道
現在,我們假定有一家公司需要處理大型數據集以生成涉及數據清理、轉換、分析和可視化的分析報告。
使用的Runnable有RunnableSequence、RunnableEach、RunnableRetry、RunnableBinding,關鍵代碼如下:
import {
RunnableSequence,
RunnableEach,
RunnableLambda,
} from "@langchain/core/runnables";
// 步驟1:通過使用重試的方式定義數據獲取
const fetchData = RunnableLambda.from(async (source) => {
// Simulate data fetching, which may fail
if (Math.random() < 0.2) {
throw new Error("Data fetch error");
}
return `Data from ${source}`;
}).withRetry({ stopAfterAttempt: 3 });
//步驟2:數據清理
const cleanData = RunnableLambda.from((data) => {
// Perform data cleaning
return `Cleaned ${data}`;
});
// 步驟3:數據轉換
const transformData = RunnableLambda.from((data) => {
// Transform data
return `Transformed ${data}`;
});
//步驟4:數據分析
const analyzeData = RunnableLambda.from((data) => {
// Analyze data
return `Analysis results of ${data}`;
});
//步驟5:數據可視化
const visualizeData = RunnableLambda.from((analysis) => {
// Generate visualization
return `Visualization of ${analysis}`;
});
//步驟6:步驟排隊
const dataProcessingSequence = RunnableSequence.from([
cleanData,
transformData,
analyzeData,
visualizeData,
]);
// 步驟7:處理多個數據源
const dataSources = ["Dataset A", "Dataset B", "Dataset C"];
const processAllData = new RunnableEach({
bound: fetchData.pipe(dataProcessingSequence),
});
// 用法
const reports = processAllData.invoke(dataSources);
// 輸出:每個數據源的可視化結果數組上述代碼中,此工作流處理來自不同來源的多個數據集的數據處理。首先,定義一個使用RunnableBinding綁定到特定數據源的fetchData可運行程序。每個數據獲取操作都使用RunnableRetry包裝,通過重試最多三次來處理瞬時故障。
從每個源獲取的數據經過RunnableSequence定義的一系列處理步驟:
- 數據清理:刪除或更正錯誤數據。
- 數據轉換:將數據轉換為適合分析的格式。
- 數據分析:執行分析計算。
- 數據可視化:生成針對分析結果的可視化表示。
在此,使用RunnableEach來并行處理多個數據集。這個對象將相同的處理順序應用于每個數據集上。
結論
總體來看,LangChain中的Runnable架構是構建涉及大型語言模型(LLM)的復雜模塊化工作流的強大基礎。在本文中,我們探討了如何創建和組合各種Runnable以應對各種挑戰:
- 路由和分支:利用RouterRunnable和RunnableBranch可以根據運行時條件實現動態執行路徑。
- 數據操作和分配:RunnableAssign、RunnablePick和RunnableMap等工具提供靈活的數據轉換功能,為后續處理步驟準備輸入。
- 序列和工作流組合:通過使用RunnableSequence、RunnableEach和RunnableParallel鏈接任務,開發人員可以協調流程,無論它們是需要順序執行還是并行處理。
- 錯誤處理和彈性:借助RunnableRetry和RunnableWithFallbacks,工作流可以優雅地處理錯誤并提供回退機制。
總之,Runnable提倡了一種結構化的方法來構建LLM代理和鏈。最后,在你計劃將LangChain集成到實際項目中時,請認真考慮Runnables如何增強你的工作流,使其更靈活、更有彈性且更易于維護。
譯者介紹
朱先忠,51CTO社區編輯,51CTO專家博客、講師,濰坊一所高校計算機教師,自由編程界老兵一枚。
原文標題:Guide to LangChain Runnable Architecture,作者:Pavlo Sobchuk






































