Jackson在Spring Boot高級(jí)應(yīng)用技巧【Long精度丟失, @JsonValue, 數(shù)據(jù)脫敏】
1.簡(jiǎn)介
- Long類型在前端缺失精度
- @JsonValue序列化單個(gè)屬性值
- 自定義注解的應(yīng)用
2. 實(shí)戰(zhàn)案例
2.1 Long精度丟失
在Web開發(fā)中,使用JavaScript處理大數(shù)值(如Long類型)時(shí),可能會(huì)遇到精度丟失的問題。這是因?yàn)镴avaScript中的數(shù)字一律采用IEEE-754標(biāo)準(zhǔn)的64位浮點(diǎn)數(shù)表示,這種格式可以很好地處理大多數(shù)數(shù)字運(yùn)算,但對(duì)于非常大的整數(shù)(超出2^53 - 1),就可能出現(xiàn)精度損失,這就非常的惡心了,可能會(huì)讓你感到莫名其妙。當(dāng)從后端獲取到Long類型的值并嘗試在前端展示時(shí),如果該值超過了JavaScript安全整數(shù)范圍,那么顯示的結(jié)果可能不準(zhǔn)確,如下示例:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/longs")
public class LongController {
@GetMapping("")
public Map<String, Object> getData() {
return Map.of("code", 0, "data", 123456789012345678L) ;
}
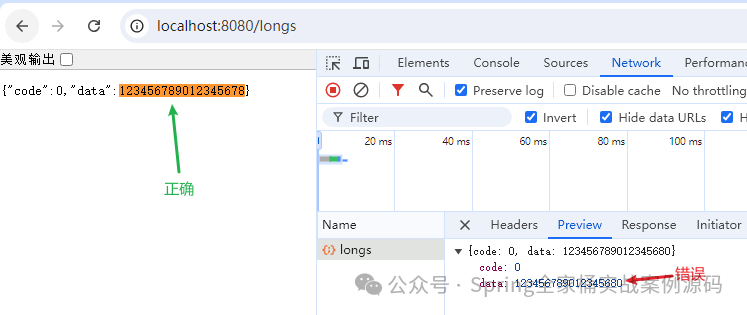
}接口返回了一個(gè)17位的Long類型數(shù)據(jù),我們先直接通過瀏覽器訪問,結(jié)果如下:
 圖片
圖片
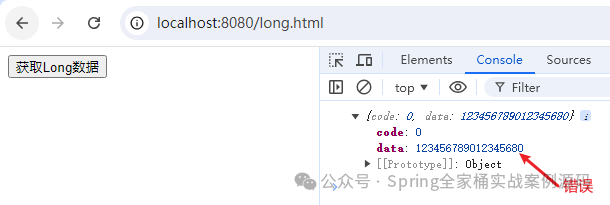
我們看到了2個(gè)結(jié)果,瀏覽器顯示的是正確的,但是通過 Network 查看數(shù)據(jù)錯(cuò)誤,接下來,我們?cè)偻ㄟ^Ajax獲取數(shù)據(jù)。
function getData() {
axios.get('http://localhost:8080/longs')
.then(resp => {
console.log(resp.data) ;
}).catch((error) => {
console.log(error) ;
});
} 圖片
圖片
在這種前后端分離的架構(gòu)下,千萬的小心,如果你返回的Long類型超過了前端number的范圍,那么將出現(xiàn)該問題。接下來要解決也是非常的簡(jiǎn)單,我們只需要進(jìn)行簡(jiǎn)單的配置即可。
@Component
public class PackMapperCustomizer implements Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilderCustomizer {
@Override
public void customize(Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder jacksonObjectMapperBuilder) {
jacksonObjectMapperBuilder.serializerByType(Long.class, ToStringSerializer.instance) ;
}
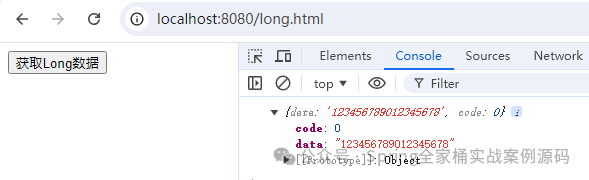
}這里我們將Long類型轉(zhuǎn)換為String類型。再次運(yùn)行上面的代碼
 圖片
圖片
通過自定義 Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilderCustomizer 屬于全局的,項(xiàng)目中所有的Long都會(huì)被轉(zhuǎn)換為String進(jìn)行輸出。這可能不是我們希望的,我們可能只是希望有針對(duì)的處理,這時(shí)候我們就可以通過注解的方式了,如下示例:
public class User {
@JsonSerialize(using = ToStringSerializer.class)
private Long id ;
private String name ;
// getters, setters
}通過上面注解的方式就能針對(duì)性的控制輸出字段類型。
2.2 @JsonValue序列化單個(gè)屬性值
@JsonValue注解用于指示一個(gè)方法,該方法將被用來轉(zhuǎn)換對(duì)象為JSON值。通常,這個(gè)方法會(huì)返回一個(gè)基本類型或其包裝類的實(shí)例,或者是其他可以直接序列化為JSON的對(duì)象。使用 @JsonValue 可以簡(jiǎn)化對(duì)象到JSON的轉(zhuǎn)換過程,使得特定屬性或計(jì)算結(jié)果能夠直接作為JSON輸出,而無需定義復(fù)雜的序列化邏輯。
現(xiàn)在有,如下的枚舉類:
public enum PaymentStatus {
NO_PAY(0, "未支付"), PAID(1, "已支付") ;
PaymentStatus(int code, String desc) {
this.code = code ;
this.desc = desc ;
}
private Integer code ;
private String desc ;
// getters, setters
}當(dāng)接口返回該枚舉類時(shí),顯示如下:
@GetMapping("")
public PaymentStatus status() {
return PaymentStatus.PAID ;
} 圖片
圖片
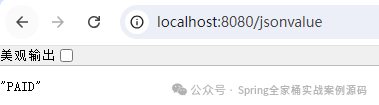
輸出了枚舉的字符串形式,如果我們要顯示具體的code或者是desc,那么我們就可以使用 @JsonValue 注解。
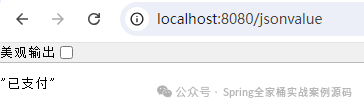
@JsonValue
private String desc ;在需要輸出的字段上添加 @JsonValue 注解即可。
 圖片
圖片
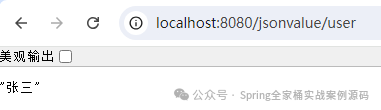
如果該注解應(yīng)用到一個(gè)普通的Java Bean對(duì)象中的某個(gè)屬性時(shí),如下示例:
public class User {
@JsonSerialize(using = ToStringSerializer.class)
private Long id ;
@JsonValue
private String name ;
}這時(shí)候接口輸出的將是name屬性對(duì)應(yīng)的值。
 圖片
圖片
2.3 自定義注解
有些時(shí)候,我們可能對(duì)輸出的某些字段要做特殊的處理在輸出到前端,比如:身份證號(hào),電話等信息,在前端展示的時(shí)候我們需要進(jìn)行脫敏處理,這時(shí)候通過自定義注解就非常的有用了。在Jackson中要自定義注解,我們可以通過@JacksonAnnotationsInside注解來實(shí)現(xiàn),如下示例:
自定義注解
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@JacksonAnnotationsInside
@JsonSerialize(using = SensitiveSerializer.class)
public @interface Sensitive {
int start() default 0 ;
int end() default 0 ;
String mask() default "*" ;
}自定義序列化處理器SensitiveSerializer
public class SensitiveSerializer extends JsonSerializer<String> implements ContextualSerializer {
private Sensitive sensitive;
@Override
public void serialize(String value, JsonGenerator gen, SerializerProvider serializers) throws IOException {
String val = value;
if (sensitive != null && StringUtils.hasLength(val)) {
String m = sensitive.mask();
int start = sensitive.start();
int end = sensitive.end();
int totalLength = value.length();
if (totalLength <= 2) {
val = totalLength == 1 ? value + m : value.substring(0, 1) + m;
} else if (totalLength <= 6) {
val = value.substring(0, 1) + String.join("", Collections.nCopies(totalLength - 2, m))
+ value.substring(totalLength - 1);
} else {
int prefixLength = Math.min(start, totalLength - 1);
int suffixLength = Math.min(end, totalLength - 1);
if (prefixLength > totalLength) {
prefixLength = totalLength / 2;
}
if (suffixLength > totalLength) {
suffixLength = totalLength / 2;
}
int maskLength = Math.max(0, totalLength - (prefixLength + suffixLength));
if (maskLength == 0) {
prefixLength -= 2;
suffixLength -= 2;
maskLength = Math.max(2, totalLength - (prefixLength + suffixLength));
}
prefixLength = Math.min(prefixLength, totalLength - 1);
suffixLength = Math.min(suffixLength, totalLength - 1);
maskLength = totalLength - prefixLength - suffixLength;
val = value.substring(0, prefixLength) + String.join("", Collections.nCopies(maskLength, m))
+ value.substring(totalLength - suffixLength);
}
}
gen.writeString(val);
}
@Override
public JsonSerializer<?> createContextual(SerializerProvider prov, BeanProperty property)
throws JsonMappingException {
sensitive = property.getAnnotation(Sensitive.class);
return this;
}
}接下來,在輸出的Java Bean中使用上面的注解。
public class User {
@JsonSerialize(using = ToStringSerializer.class)
private Long id ;
private String name ;
@Sensitive(start = 6, end = 4)
private String idCard ;
@Sensitive(start = 4, end = 3)
private String phone ;
// getters, setters
}最后,在前端展示結(jié)果如下:
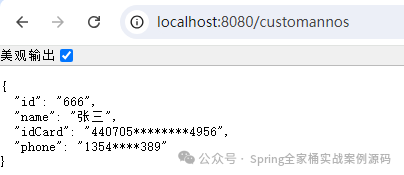
敏感數(shù)據(jù)得到了脫敏處理。