聊聊 Redis 集群 Gosisp 協議與節點通信
一、數據分片與分配算法
為了應對流量并發瓶頸,以及方便數據遷移與擴容,數據分片方式是常用的解決方式。
Kafka的分區(partition)、RocketMQ的隊列(Queue)、Elasticsearch的主分片/副本(shard)、數據庫的分庫分表等,均采用數據分片思想應對高并發流量。
Redis的集群模式也不例外,采用虛擬槽slot實現數據分片。
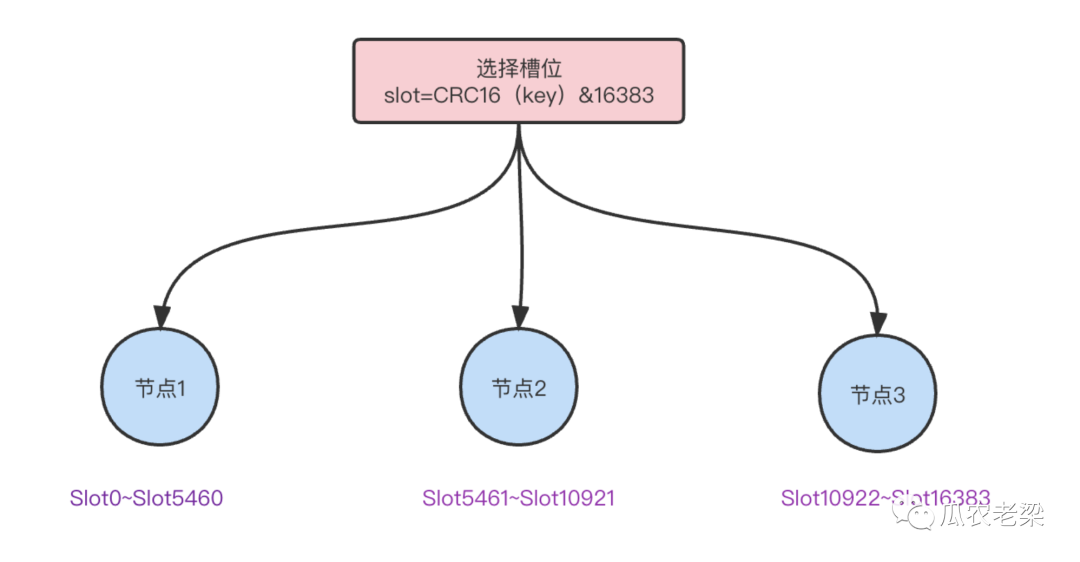
Redis的槽位范圍0~16383,共16384個槽位。
Redis Cluster中每個節點負責一部分槽數量,分配算法:slot=CRC16(key)&16383。
槽位分配與選擇示意圖如下:
二、Gosisp協議類型與格式
1、Gosisp協議類型
節點通信使用Gosisp協議,消息類型有:ping消息、pong消息、meet消息、fail消息。
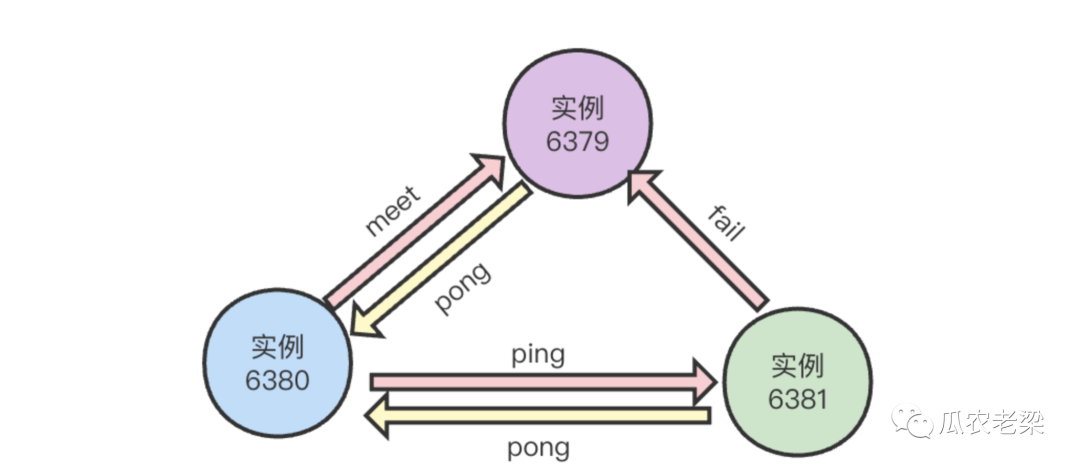
- MEET消息:當新節點加入時握手使用。
- PING消息:節點之間周期性地發送ping消息、交換狀態。
- PONG消息:收到meet、ping消息的響應、并封裝自身狀態消息。
- FAIL消息:當節點下線時,像集群廣播一個fail消息,其他節點收到會更新該節點的狀態。
通信端口=節點端口+10000。
每個節點周期性的選擇幾個節點發送ping消息。
2.消息頭格式
消息頭的結構在clusterMsg中,具體屬性如下:
字段 | 說明 | 簡述 |
char sig[4] | Signature "RCmb" (Redis Cluster message bus). | 信號簽名 |
uint32_t totlen | Total length of this message | 消息長度 |
uint16_t ver | Protocol version, currently set to 1 | 協議版本 |
uint16_t port | TCP base port number | 端口信息 |
uint16_t type | Message type | 消息類型,ping、meet、pong等 |
uint16_t count | Only used for some kind of messages | 消息體包含的節點數量 |
uint64_t currentEpoch | The epoch accordingly to the sending node | 發送節點的紀元(epoch)配置 |
uint64_t configEpoch | The config epoch if it's a master, or the last epoch advertised by its master if it is a slave | 主從節點中,主節點的紀元配置 |
uint64_t offset | Master replication offset if node is a master or processed replication offset if node is a slave | 復制偏移量 |
char sender[CLUSTER_NAMELEN] | Name of the sender node | 發送節點的nodeId信息 |
unsigned char myslots[CLUSTER_SLOTS/8] | myslots info | 發送節點負責的槽位信息 |
char slaveof[CLUSTER_NAMELEN] | 從節點的nodeId信息 | |
char myip[NET_IP_STR_LEN] | Sender IP, if not all zeroed | 發送者IP |
uint16_t extensions | Number of extensions sent along with this packet | 擴展信息 |
char notused1[30] | 30 bytes reserved for future usage | 保留30個字節擴展供未來使用 |
uint16_t pport | Sender TCP plaintext port, if base port is TLS | 如果基礎端口為TLS,TCP的明文端口 |
uint16_t cport | Sender TCP cluster bus port | 發送者TCP集群總線端口 |
uint16_t flags | Sender node flags | 發送節點標識,區分主從以及是否下線 |
unsigned char state | Cluster state from the POV of the sender | 發送者角度的集群狀態 |
unsigned char mflags[3] | Message flags: CLUSTERMSG_FLAG[012]_... | 消息標識 |
union clusterMsgData data | 消息體正文 |
3.消息體格式
消息體clusterMsgData結構如下:
union clusterMsgData {
/* PING, MEET and PONG */
struct {
/* Array of N clusterMsgDataGossip structures */
clusterMsgDataGossip gossip[1];
/* Extension data that can optionally be sent for ping/meet/pong
* messages. We can't explicitly define them here though, since
* the gossip array isn't the real length of the gossip data. */
} ping;
/* FAIL */
struct {
clusterMsgDataFail about;
} fail;
/* PUBLISH */
struct {
clusterMsgDataPublish msg;
} publish;
/* UPDATE */
struct {
clusterMsgDataUpdate nodecfg;
} update;
/* MODULE */
struct {
clusterMsgModule msg;
} module;
};
備注:clusterMsgDataGossip:PING, MEET and PONG采用的消息結構體,詳細如下。
typedef struct {
char nodename[CLUSTER_NAMELEN];
uint32_t ping_sent;
uint32_t pong_received;
char ip[NET_IP_STR_LEN]; /* IP address last time it was seen */
uint16_t port; /* base port last time it was seen */
uint16_t cport; /* cluster port last time it was seen */
uint16_t flags; /* node->flags copy */
uint16_t pport; /* plaintext-port, when base port is TLS */
uint16_t notused1;
} clusterMsgDataGossip;
- nodename:節點NodeId
- ping_sent:最后一次向該節點發送ping消息時間
- pong_received:最后一次接受該節點pong消息時間
- ip/port/cport/flags/pport:IP端口以及節點標識
三、節點選擇與通信流程
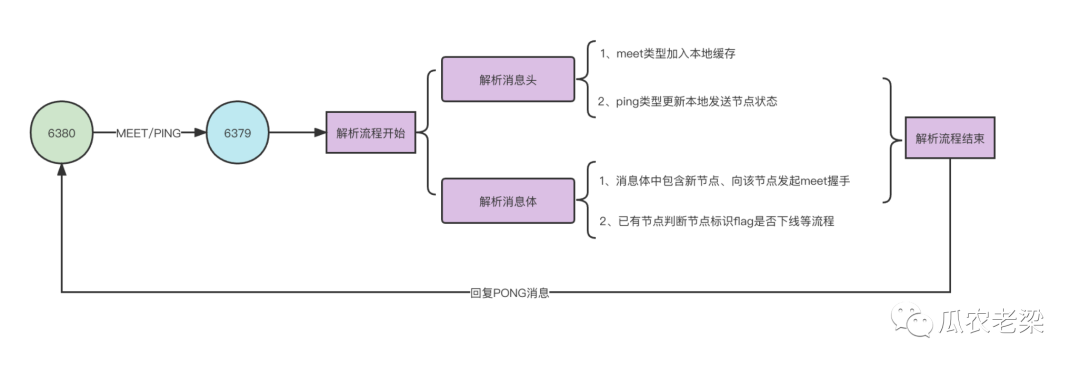
1.節點通信流程
兩個節點之間發送MEET/PING消息,回復PONG消息的流程如下。
2.通信節點選擇
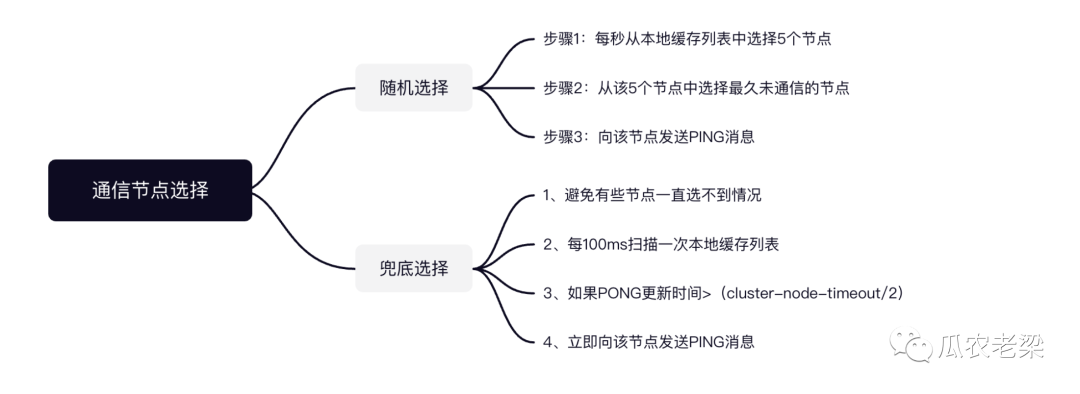
Gosisp協議PING/PONG通信時,具體選擇哪個節點發起通信?
每秒從本地實例列表選擇5個節點,在這5個節點中選擇最久沒有通信的實例,向該實例發送PING消息。
避免一些實例節點一直選不到,會有一個定時任務掃描兜底措施。
集群內部每秒10次的固定頻率掃描本地緩存節點列表,也就是每100ms一次。
如果節點:PONG更新時間>(cluster-node-timeout/2)立即向該節點發送PING消息。
cluster-node-timeout是判定實例故障的心跳超時時間,默認15秒。