Java 8 異步編程 CompletableFuture 全解析
本文轉載自微信公眾號「KK架構師」,作者wangkai 。轉載本文請聯系KK架構師公眾號。
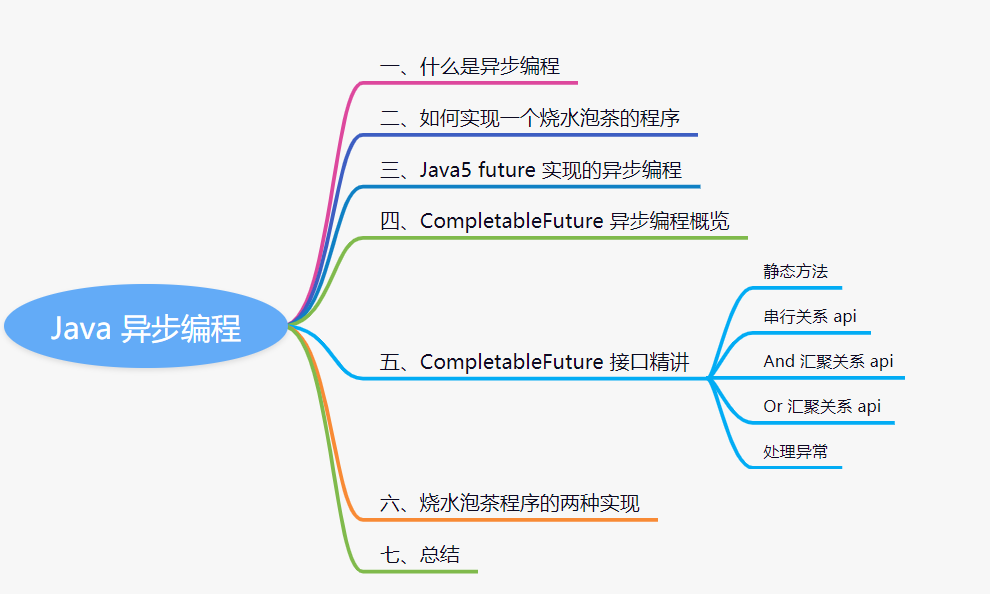
本文大綱速看
一、異步編程
通常來說,程序都是順序執行,同一時刻只會發生一件事情。如果一個函數依賴于另一個函數的結果,它只能等待那個函數結束才能繼續執行,從用戶角度來說,整個程序才算執行完畢。但現在的計算機普遍擁有多核 CPU,在那里干等著毫無意義,完全可以在另一個處理器內核上干其他工作,耗時長的任務結束之后會主動通知你。這就是異步編程的出發點:充分使用多核 CPU 的優勢,最大程度提高程序性能。一句話來說:所謂異步編程,就是實現一個無需等待被調用函數的返回值而讓操作繼續運行的方法。
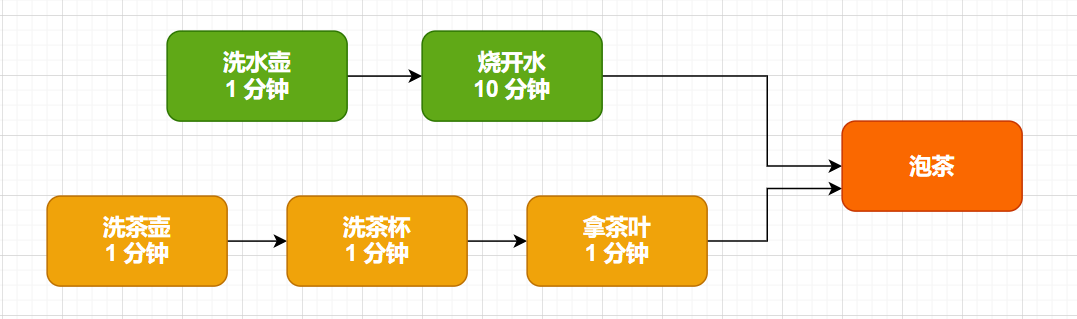
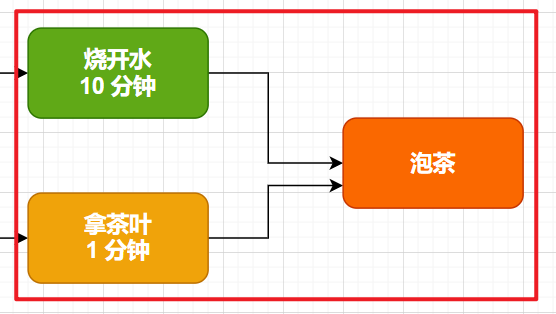
二、拋出一個問題:如何實現燒水泡茶的程序
最后我們會使用傳統方式和 Java8 異步編程方式分別實現,來對比一下實現復雜度。
三、Java5 的 Future 實現的異步編程
Future 是 Java 5 添加的類,用來描述一個異步計算的結果。你可以使用 isDone() 方法檢查計算是否完成,或者使用 get() 方法阻塞住調用線程,直到計算完成返回結果,也可以使用 cancel() 方法停止任務的執行。
- public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
- ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
- Future<Integer> f = es.submit(() -> 100);
- System.out.println(f.get());
- es.shutdown();
- }
雖然 Future 提供了異步執行任務的能力,但是對于結果的獲取卻是很不方便,只能通過阻塞或者輪詢的方式得到任務的結果。阻塞的方式顯然和我們異步編程的初衷相違背,輪詢的方式又會耗費無謂的 CPU 資源,而且也不能及時的獲取結果。
當然,很多其他的語言采用回調的方式來實現異步編程,比如 Node.js;Java 的一些框架,比如 Netty,Google Guava 也擴展了 Future 接口,提供了很多回調的機制,封裝了工具類,輔助異步編程開發。
Java 作為老牌編程語言,自然也不會落伍。在 Java 8 中,新增了一個包含 50 多個方法的類:CompletableFuture,提供了非常強大的 Future 擴展功能,可以幫助我們簡化異步編程的復雜性,提供函數式編程的能力。
四、CompletableFuture 類功能概覽
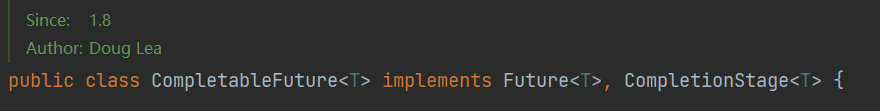
如下圖是 CompletableFuture 實現的接口:
它實現了 Future 接口,擁有 Future 所有的特性,比如可以使用 get() 方法獲取返回值等;還實現了 CompletionStage 接口,這個接口有超過 40 個方法,功能太豐富了,它主要是為了編排任務的工作流。
我們可以把工作流和工作流之間的關系分類為三種:串行關系,并行關系,匯聚關系。
串行關系
提供了如下的 api 來實現(先大致瀏覽一遍):
- CompletionStage<R> thenApply(fn);
- CompletionStage<R> thenApplyAsync(fn);
- CompletionStage<Void> thenAccept(consumer);
- CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(consumer);
- CompletionStage<Void> thenRun(action);
- CompletionStage<Void> thenRunAsync(action);
- CompletionStage<R> thenCompose(fn);
- CompletionStage<R> thenComposeAsync(fn);
并行關系
多線程異步執行就是并行關系
匯聚關系
匯聚關系,又分為 AND 匯聚關系和 OR 匯聚關系:
AND 匯聚關系,就是所有依賴的任務都完成之后再執行;OR 匯聚關系,就是依賴的任務中有一個執行完成,就開始執行。
AND 匯聚關系由這些接口表達:
- CompletionStage<R> thenCombine(other, fn);
- CompletionStage<R> thenCombineAsync(other, fn);
- CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBoth(other, consumer);
- CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(other, consumer);
- CompletionStage<Void> runAfterBoth(other, action);
- CompletionStage<Void> runAfterBothAsync(other, action);
OR 匯聚關系由這些接口來表達:
- CompletionStage applyToEither(other, fn);
- CompletionStage applyToEitherAsync(other, fn);
- CompletionStage acceptEither(other, consumer);
- CompletionStage acceptEitherAsync(other, consumer);
- CompletionStage runAfterEither(other, action);
- CompletionStage runAfterEitherAsync(other, action);
五、CompletableFuture 接口精講
1、提交執行的靜態方法
方法名描述
| 方法名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| runAsync(Runnable runnable) | 執行異步代碼,使用 ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 作為它的線程池 |
| runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor) | 執行異步代碼,使用指定的線程池 |
| supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier) | 異步執行代碼,有返回值,使用 ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 作為它的線程池 |
| supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor) | 異步執行代碼,有返回值,使用指定的線程池執行 |
上述四個方法,都是提交任務的,runAsync 方法需要傳入一個實現了 Runnable 接口的方法,supplyAsync 需要傳入一個實現了 Supplier 接口的方法,實現 get 方法,返回一個值。
(1)run 和 supply 的區別
run 就是執行一個方法,沒有返回值,supply 執行一個方法,有返回值。
(2)一個參數和兩個參數的區別
第二個參數是線程池,如果沒有傳,則使用自帶的 ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 作為線程池,這個線程池默認創建的線程數是 CPU 的核數(也可以通過 JVM option:-Djava.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.common.parallelism 來設置 ForkJoinPool 線程池的線程數)
2、串行關系 api
這些 api 之間主要是能否獲得前一個任務的返回值與自己是否有返回值的區別。
| api | 是否可獲得前一個任務的返回值 | 是否有返回值 |
|---|---|---|
| thenApply | 能 | 有 |
| thenAccept | 能 | 無 |
| thenRun | 不能 | 無 |
| thenCompose | 能 | 有 |
(1) thenApply 和 thenApplyAsync 使用
thenApply 和 thenApplyAsync 把兩個并行的任務串行化,另一個任務在獲得上一個任務的返回值之后,做一些加工和轉換。它也是有返回值的。
- public class BasicFuture4 {
- @Data
- @AllArgsConstructor
- @ToString
- static class Student {
- private String name;
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
- CompletableFuture<Student> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Jack")
- .thenApply(s -> s + " Smith")
- .thenApply(String::toUpperCase)
- .thenApplyAsync(Student::new);
- System.out.println(future.get());
- }
- }
結果可以看到,輸入是一個字符串,拼接了一個字符串,轉換成大寫,new 了一個 Student 對象返回。
- BasicFuture4.Student(name=JACK SMITH)
和 thenApply 一起的還有 thenAccept 和 thenRun,thenAccept 能獲得到前一個任務的返回值,但是自身沒有返回值;thenRun 不能獲得前一個任務的返回值,自身也沒有返回值。
(2)thenApply 和 thenApplyAsync 的區別
這兩個方法的區別,在于誰去執行任務。如果使用 thenApplyAsync,那么執行的線程是從 ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 或者自己定義的線程池中取線程去執行。如果使用 thenApply,又分兩種情況,如果 supplyAsync 方法執行速度特別快,那么 thenApply 任務就使用主線程執行,如果 supplyAsync 執行速度特別慢,就是和 supplyAsync 執行線程一樣。
可以使用下面的例子演示一下:
- package com.dsj361.future;
- import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
- import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
- /**
- * @Author wangkai
- */
- public class BasicFuture8 {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
- System.out.println("----------supplyAsync 執行很快");
- CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
- System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
- return "1";
- }).thenApply(s -> {
- System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
- return "2";
- });
- System.out.println(future1.get());
- System.out.println("----------supplyAsync 執行很慢");
- CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
- try {
- Thread.sleep(1000);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- }
- System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
- return "1";
- }).thenApply(s -> {
- System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
- return "2";
- });
- System.out.println(future2.get());
- }
- }
執行結果:
- ----------supplyAsync 執行很快
- ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1
- main
- 2
- ----------supplyAsync 執行很慢
- ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1
- ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1
- 2
(3)thenCompose 的使用
假設有兩個異步任務,第二個任務想要獲取第一個任務的返回值,并且做運算,我們可以用 thenCompose。此時使用 thenApply 也可以實現,看一段代碼發現他們的區別:
- public class BasicFuture9 {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
- CompletableFuture<String> future = getLastOne().thenCompose(BasicFuture9::getLastTwo);
- System.out.println(future.get());
- CompletableFuture<CompletableFuture<String>> future2 = getLastOne().thenApply(s -> getLastTwo(s));
- System.out.println(future2.get().get());
- }
- public static CompletableFuture<String> getLastOne(){
- return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()-> "topOne");
- }
- public static CompletableFuture<String> getLastTwo(String s){
- return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()-> s + " topTwo");
- }
- }
可以看到使用 thenApply 的時候,需要使用兩個 get() 方法才能獲取到最終的返回值,使用 thenCompose 只要一個即可。
3、And 匯聚關系 Api
(1)thenCombine 的使用
加入我們要計算兩個異步方法返回值的和,就必須要等到兩個異步任務都計算完才能求和,此時可以用 thenCombine 來完成。
- public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
- CompletableFuture<Integer> thenComposeOne = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 192);
- CompletableFuture<Integer> thenComposeTwo = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 196);
- CompletableFuture<Integer> thenComposeCount = thenComposeOne
- .thenCombine(thenComposeTwo, (s, y) -> s + y);
- thenComposeOne.thenAcceptBoth(thenComposeTwo,(s,y)-> System.out.println("thenAcceptBoth"));
- thenComposeOne.runAfterBoth(thenComposeTwo, () -> System.out.println("runAfterBoth"));
- System.out.println(thenComposeCount.get());
- }
可以看到 thenCombine 第二個參數是一個 Function 函數,前面兩個異步任務都完成之后,使用這個函數來完成一些運算。
(2)thenAcceptBoth
接收前面兩個異步任務的結果,執行一個回調函數,但是這個回調函數沒有返回值。
(3)runAfterBoth
接收前面兩個異步任務的結果,但是回調函數,不接收參數,也不返回值。
4、Or 匯聚關系 Api
- public class BasicFuture11 {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
- CompletableFuture<Integer> thenComposeOne = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 192);
- CompletableFuture<Integer> thenComposeTwo = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 196);
- CompletableFuture<Integer> thenComposeCount = thenComposeOne
- .applyToEither(thenComposeTwo, s -> s + 1);
- thenComposeOne.acceptEither(thenComposeTwo,s -> {});
- thenComposeOne.runAfterEither(thenComposeTwo,()->{});
- System.out.println(thenComposeCount.get());
- }
- }
(1)applyToEither
任何一個執行完就執行回調方法,回調方法接收一個參數,有返回值
(2)acceptEither
任何一個執行完就執行回調方法,回調方法接收一個參數,無返回值
(3)runAfterEither
任何一個執行完就執行回調方法,回調方法不接收參數,也無返回值
5、處理異常
上面我們講了如何把幾個異步任務編排起來,執行一些串行或者匯聚操作。還有一個重要的地方,就是異常的處理。
先看下面的例子:
- public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
- CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
- System.out.println("execute one ");
- return 100;
- })
- .thenApply(s -> 10 / 0)
- .thenRun(() -> System.out.println("thenRun"))
- .thenAccept(s -> System.out.println("thenAccept"));
- CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> System.out.println("other"));
- }
結果:
- execute one
- other
可以發現,只要鏈條上有一個任務發生了異常,這個鏈條下面的任務都不再執行了。
但是 main 方法上的接下來的代碼還是會執行的。
所以這個時候,需要合理的去處理異常來完成一些收尾的工作。
- public class BasicFuture12 {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
- CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
- System.out.println("execute one ");
- return 100;
- })
- .thenApply(s -> 10 / 0)
- .thenRun(() -> System.out.println("thenRun"))
- .thenAccept(s -> System.out.println("thenAccept"))
- .exceptionally(s -> {
- System.out.println("異常處理");
- return null;
- });
- CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> System.out.println("other"));
- }
- }
可以使用 exceptionally 來處理異常。
使用 handle() 方法也可以處理異常。但是 handle() 方法的不同之處在于,即使沒有發生異常,也會執行。
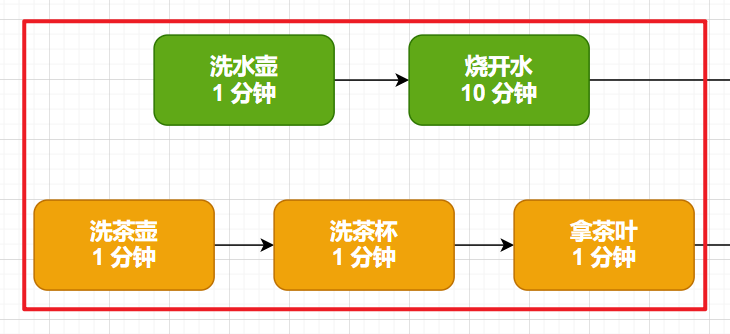
六、燒水泡茶程序的實現
1、使用 Thread 多線程和 CountDownLatch 來實現
- public class MakeTee {
- private static CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(2);
- static class HeatUpWater implements Runnable {
- private CountDownLatch countDownLatch;
- public HeatUpWater(CountDownLatch countDownLatch) {
- this.countDownLatch = countDownLatch;
- }
- @Override
- public void run() {
- try {
- System.out.println("洗水壺");
- Thread.sleep(1000);
- System.out.println("燒開水");
- Thread.sleep(5000);
- countDownLatch.countDown();
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- }
- }
- }
- static class PrepareTee implements Runnable {
- private CountDownLatch countDownLatch;
- public PrepareTee(CountDownLatch countDownLatch) {
- this.countDownLatch = countDownLatch;
- }
- @Override
- public void run() {
- try {
- System.out.println("洗茶壺");
- Thread.sleep(1000);
- System.out.println("洗茶杯");
- Thread.sleep(1000);
- System.out.println("拿茶葉");
- Thread.sleep(1000);
- countDownLatch.countDown();
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- }
- }
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
- new Thread(new HeatUpWater(countDownLatch) ).start();
- new Thread(new PrepareTee(countDownLatch)).start();
- countDownLatch.await();
- System.out.println("準備就緒,開始泡茶");
- }
- }
這里我們使用兩個線程,分別執行燒水和泡茶的程序,使用 CountDownLatch 來協調兩個線程的進度,等到他們都執行完成之后,再執行泡茶的動作。
可以看到這種方法,多了很多不必要的代碼,new Thread,人工維護 CountDownLatch 的進度。
2、使用 CompletableFuture 來實現
- public class MakeTeeFuture {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
- CompletableFuture<Void> future1 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
- try {
- System.out.println("洗水壺");
- Thread.sleep(1000);
- System.out.println("燒開水");
- Thread.sleep(5000);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- });
- CompletableFuture<Void> future2 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
- try {
- System.out.println("洗茶壺");
- Thread.sleep(1000);
- System.out.println("洗茶杯");
- Thread.sleep(1000);
- System.out.println("拿茶葉");
- Thread.sleep(1000);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- });
- CompletableFuture<Void> finish = future1.runAfterBoth(future2, () -> {
- System.out.println("準備完畢,開始泡茶");
- });
- System.out.println(finish.get());
- }
- }
這個程序極度簡單,無需手工維護線程,給任務分配線程的工作也不需要關注。
同時語義也更加清晰,future1.runAfterBoth(future2,......) 能夠清晰的表述“任務 3 要等到任務 1 和任務 2 都完成之后才能繼續開始”
然后代碼更加簡練并且專注于業務邏輯,幾乎所有的代碼都是業務邏輯相關的。
七、總結
本文介紹了異步編程的概念,以及 Java8 的 CompletableFuture 是如何優雅的處理多個異步任務之間的協調工作的。CompletableFuture 能夠極大簡化我們對于異步任務編排的工作,Flink 在提交任務時,也是使用這種異步任務的方式,去編排提交時和提交后對于任務狀態處理的一些工作的。